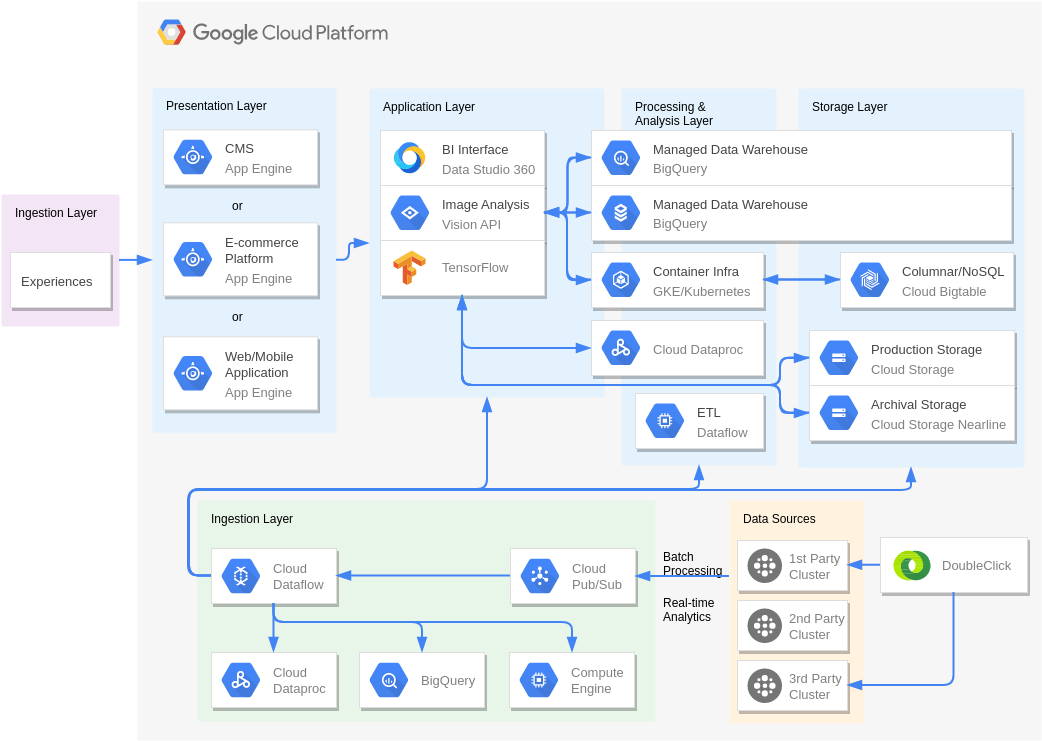
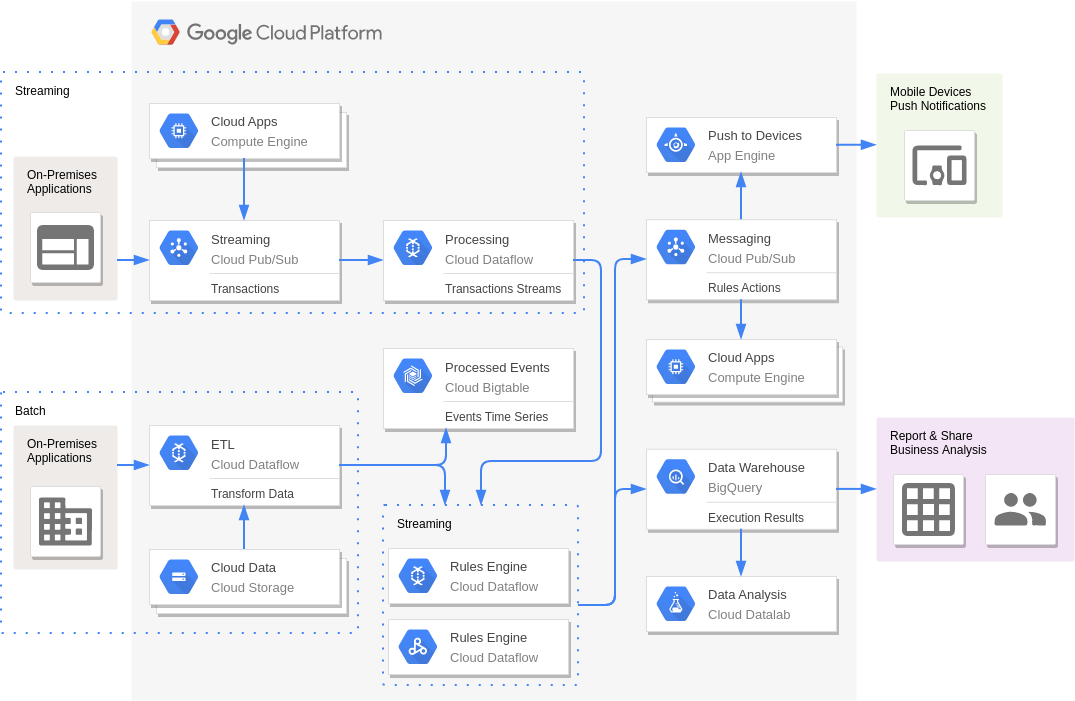
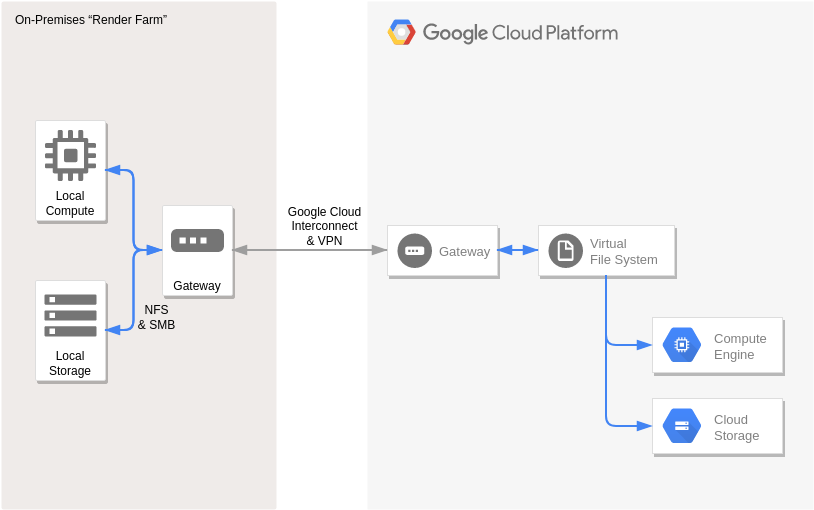
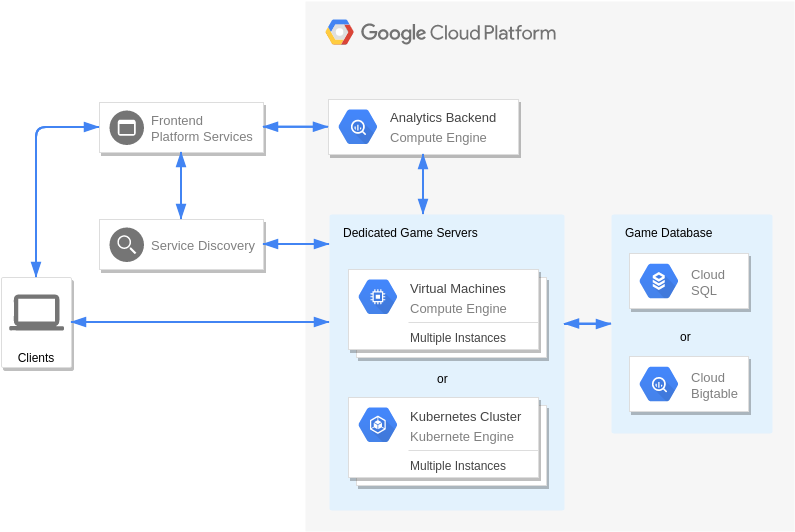
Navigating the Cloud: Unveiling the Google Cloud Platform Diagram
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, businesses and developers seek robust solutions to meet their diverse needs. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) stands as a formidable player in this arena, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud services. Understanding the intricacies of GCP can be daunting, but a well-crafted diagram can serve as a navigational guide through the cloud.
Key Components of the Google Cloud Platform Diagram
- Compute Engine: At the core of GCP’s infrastructure, the Compute Engine provides scalable virtual machines (VMs) for running applications. Represented in the diagram as interconnected server icons, this component is the powerhouse of computation in the cloud.
- App Engine: Pictorially depicted as a scalable gear, the App Engine allows developers to build and deploy applications without the burden of managing the underlying infrastructure. It’s the go-to option for those seeking a fully managed, serverless platform.
- Kubernetes Engine: Recognizable by its cluster of interconnected containers, the Kubernetes Engine enables efficient orchestration and management of containerized applications. It’s a vital component for those embracing containerization and microservices architecture.
- Cloud Functions: Shown as small, nimble clouds, Cloud Functions represent serverless functions that automatically scale in response to incoming traffic. This component is ideal for executing individual functions without the need to provision or manage servers.
- Storage Options: GCP provides various storage solutions, each depicted differently in the diagram. Cloud Storage is illustrated as a storage box, Cloud SQL as a database icon, and Bigtable as a distributed storage symbol. This section emphasizes the flexibility GCP offers for diverse data storage requirements.
- Networking: Illustrated as interconnected lines and nodes, the networking components showcase GCP’s emphasis on creating robust and secure connections. Google Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows users to customize their network and control communication between resources.
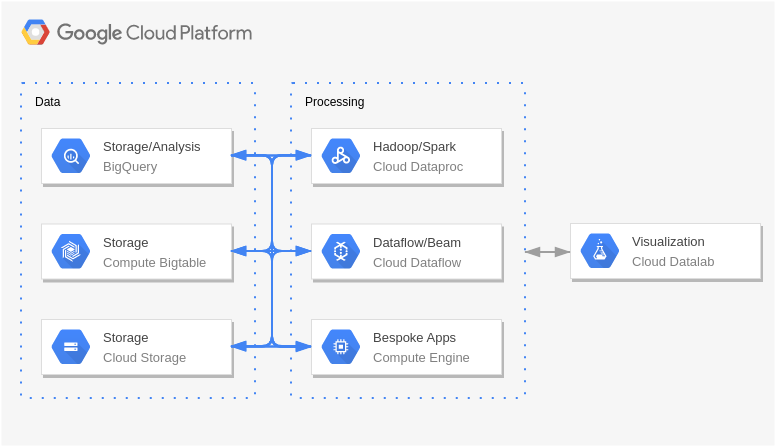
- Big Data and Analytics: Depicted as a data pipeline, GCP’s Big Data and Analytics services include BigQuery, Dataflow, and Dataprep. These services empower users to analyze and derive insights from large datasets efficiently.
- AI and Machine Learning: Symbolized by a neural network icon, GCP’s AI and Machine Learning services are integral to the platform. TensorFlow and AI Platform are tools that developers can leverage to build, train, and deploy machine learning models.
- Identity and Security: Represented as a lock and key, GCP’s Identity and Security components, including Identity and Access Management (IAM), emphasize the platform’s commitment to robust security measures. IAM allows fine-grained control over who can access resources and what actions they can perform.
Examples
Disaster Recovery with Application Replication
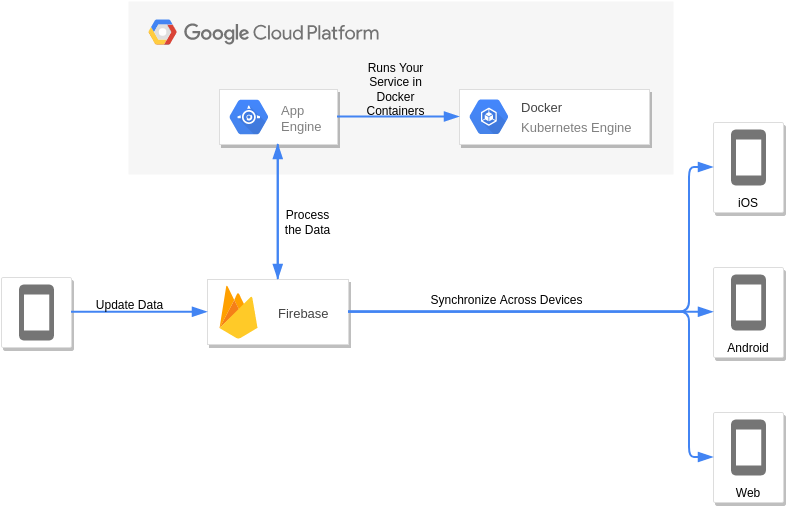
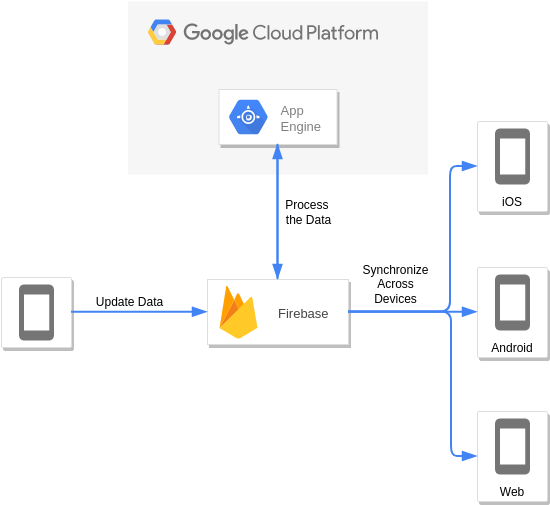
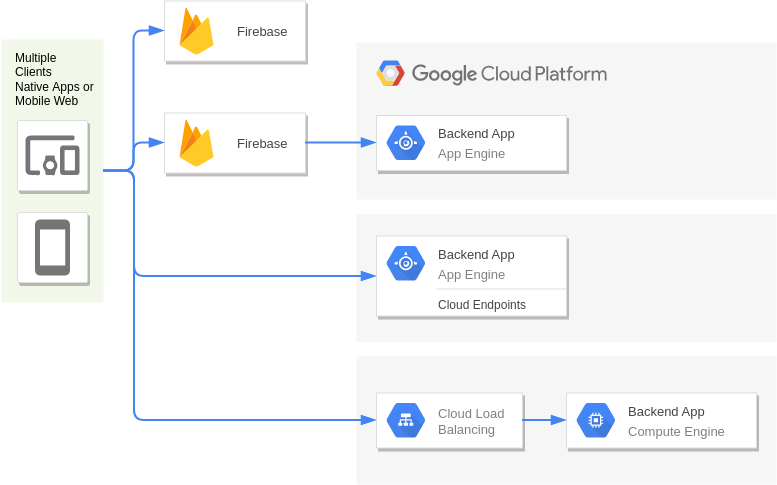
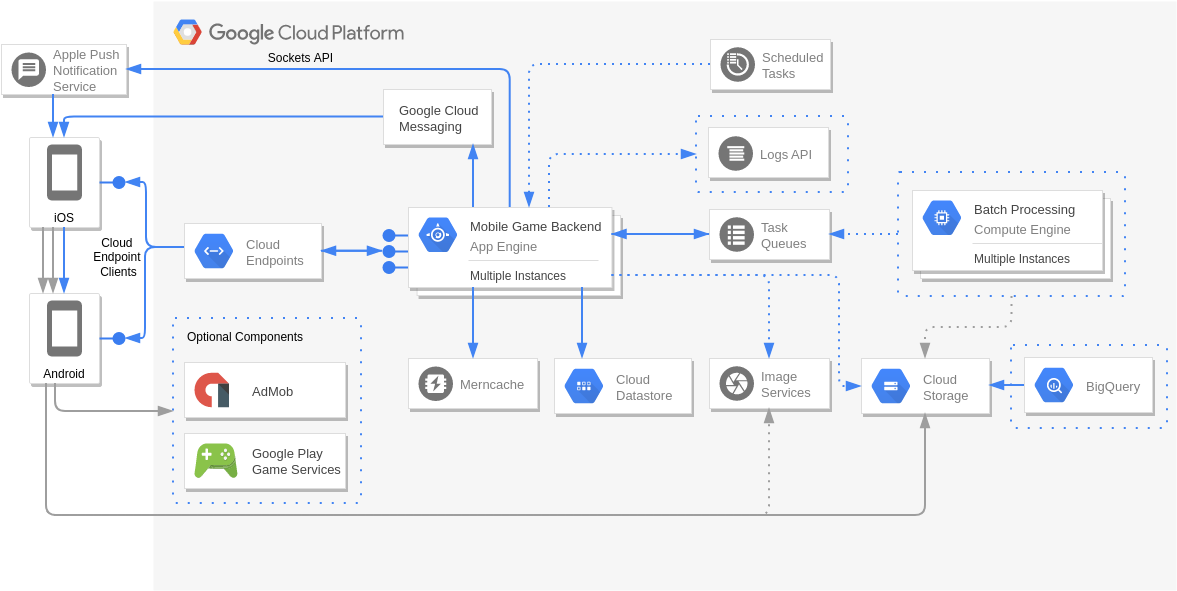
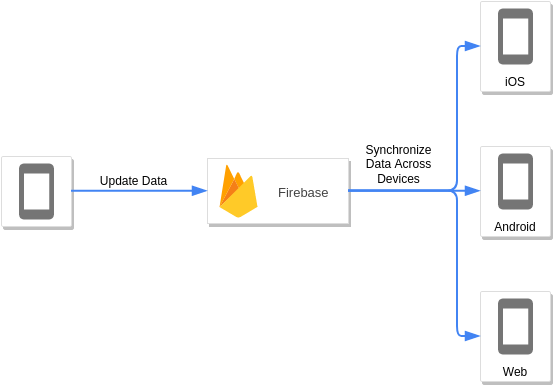
Firebase and Google App Engine
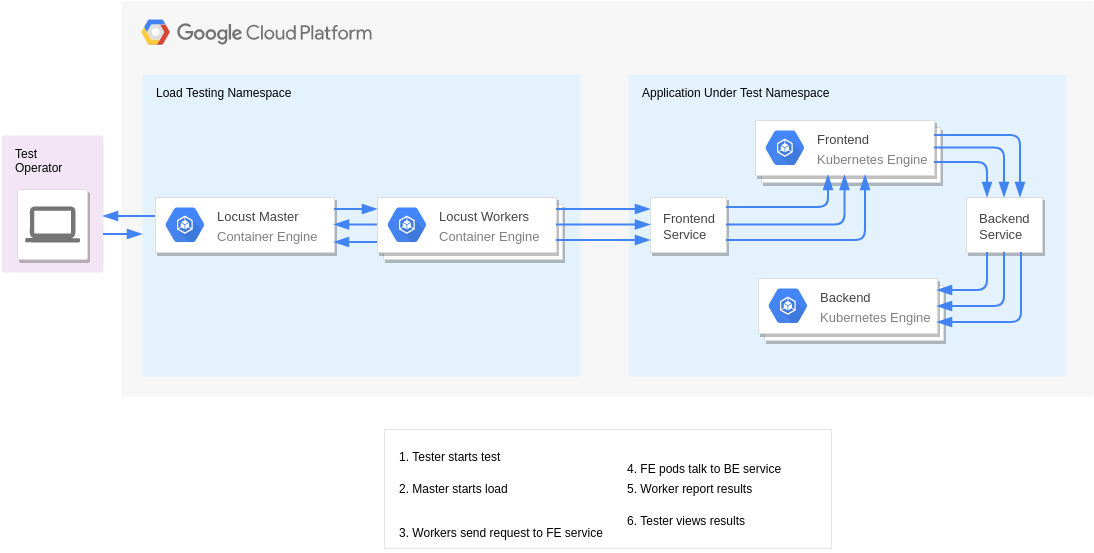
Scale Testing with Kubernetes+Locust
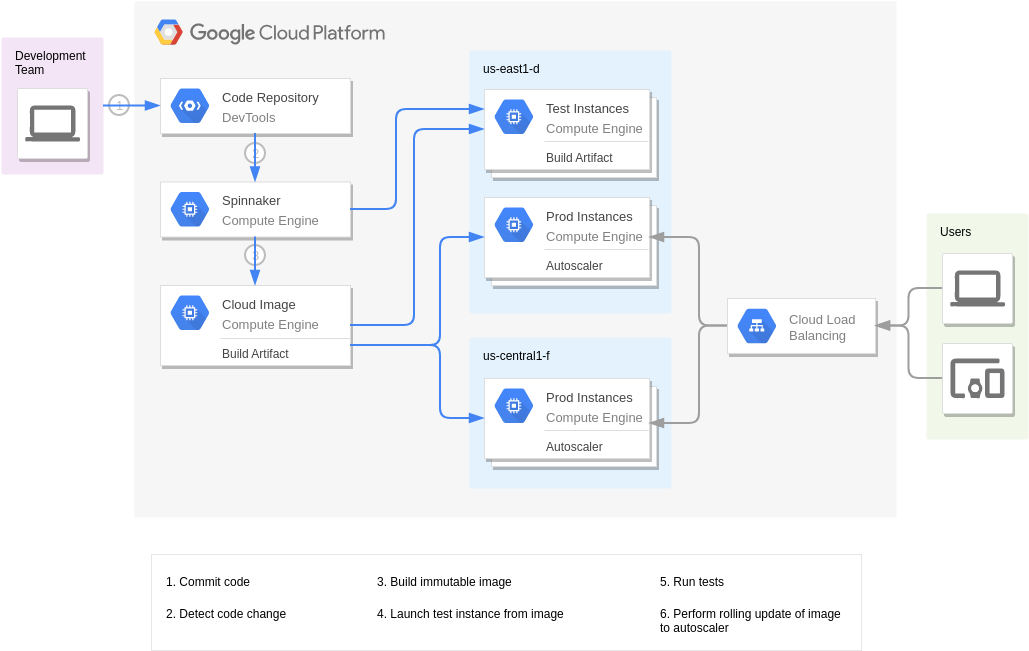
Continuous Delivery with Spinnaker
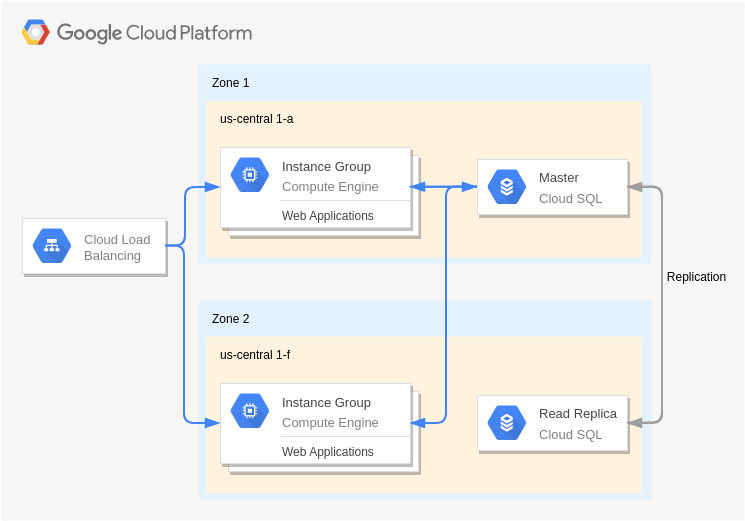
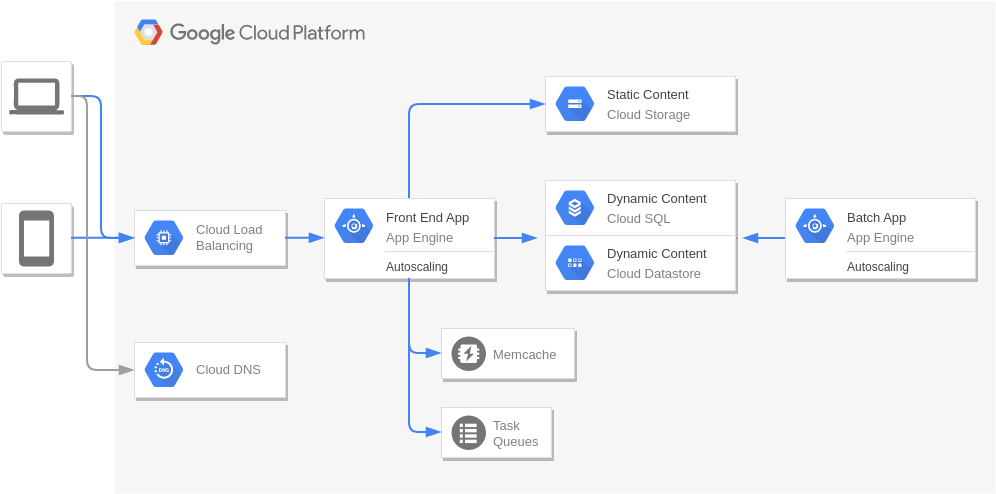
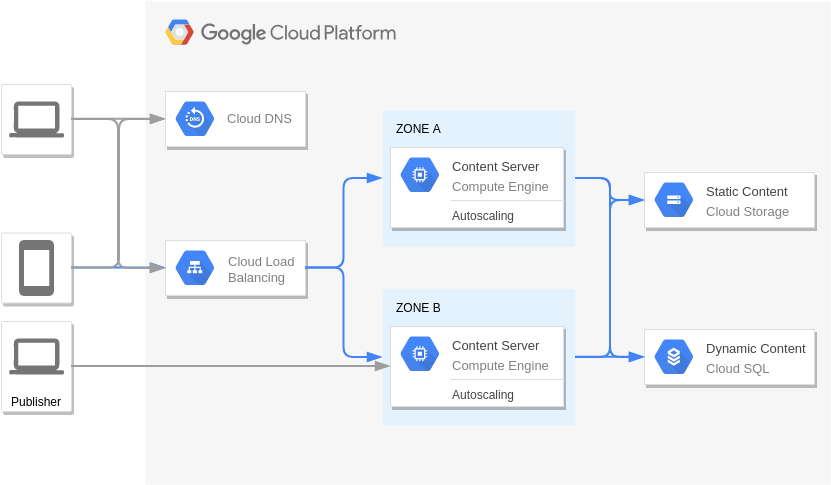
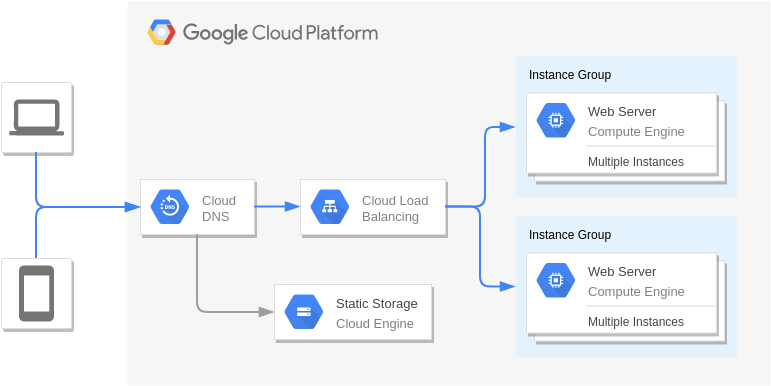
Web Application on Google App Engine
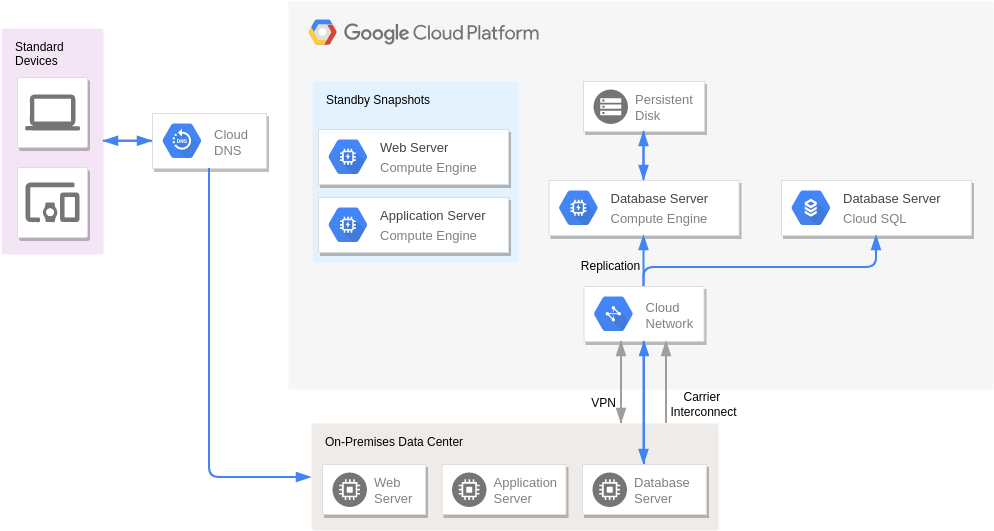
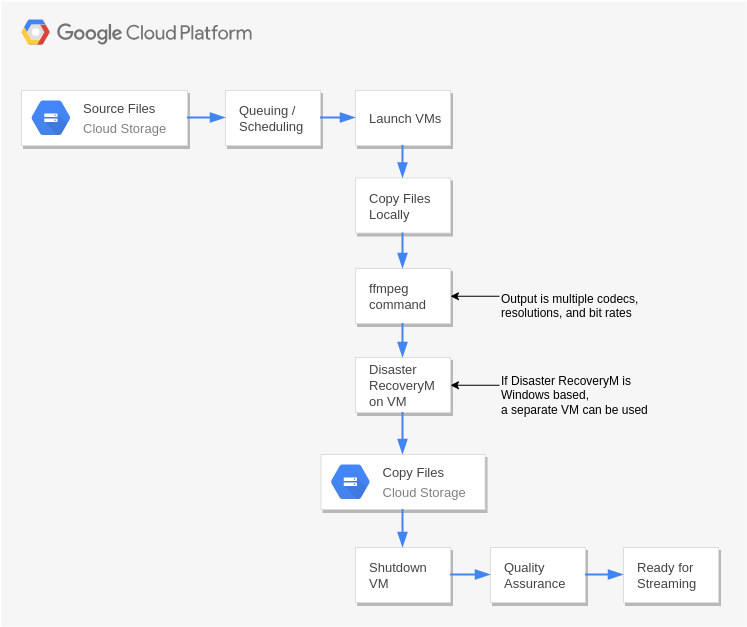
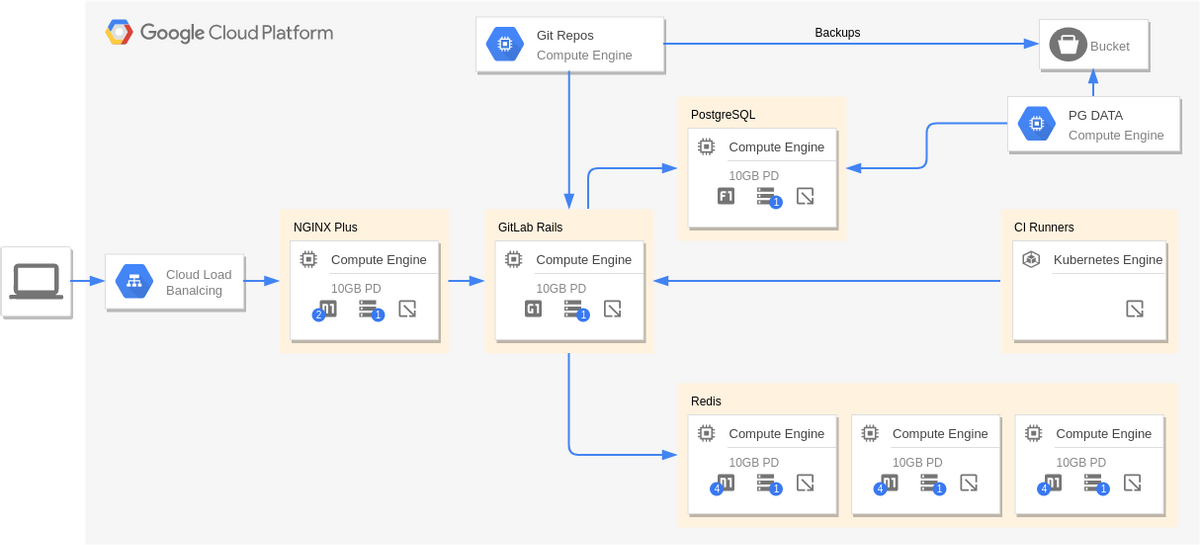
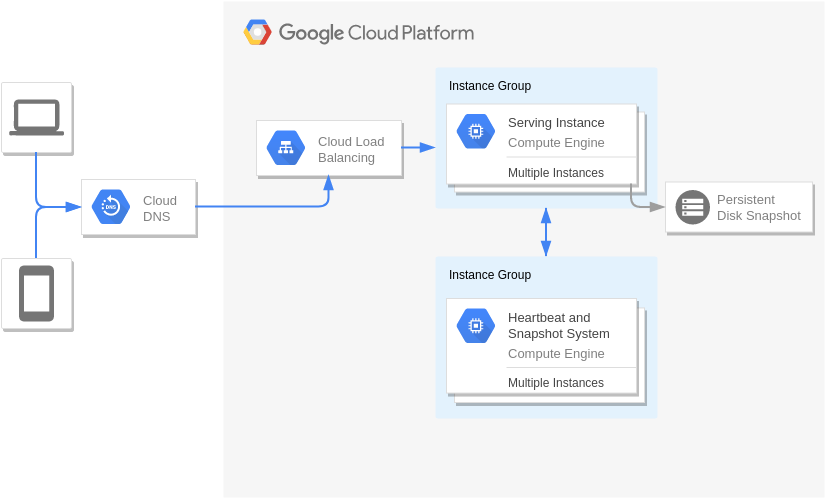
Disaster Recovery with Application Replication
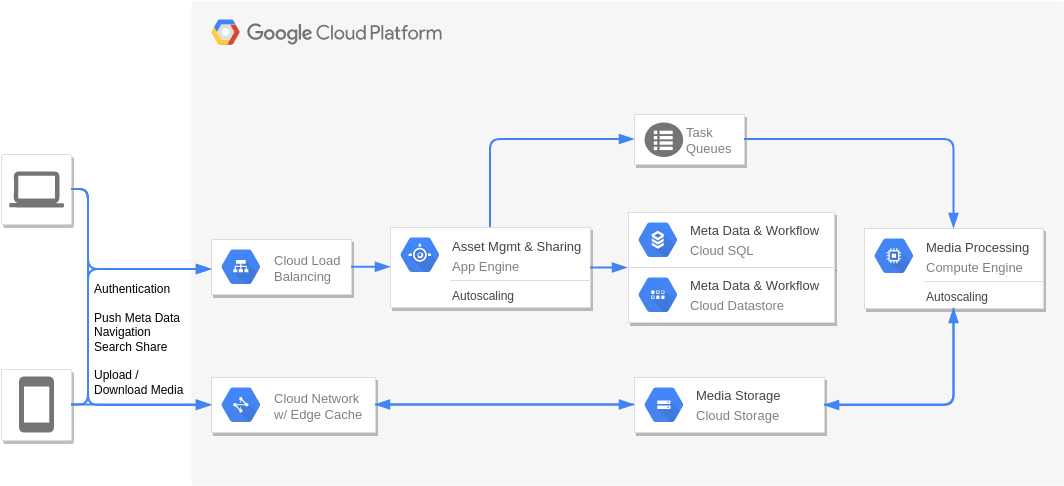
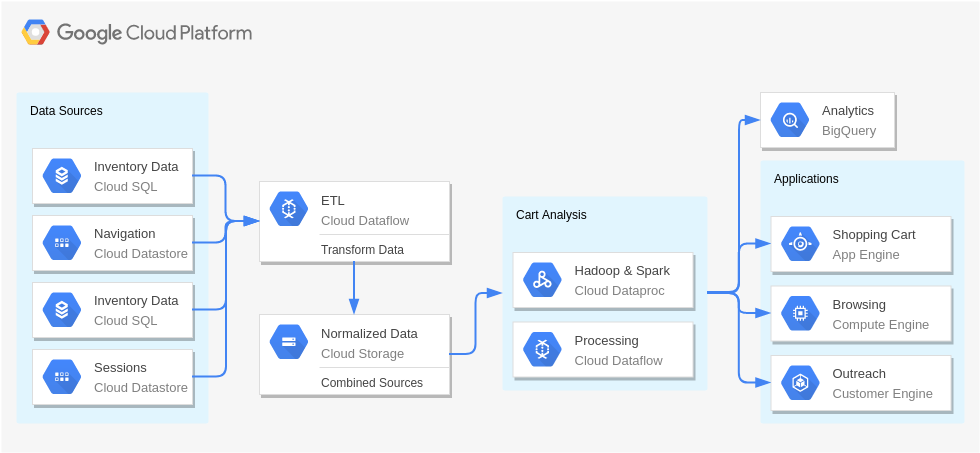
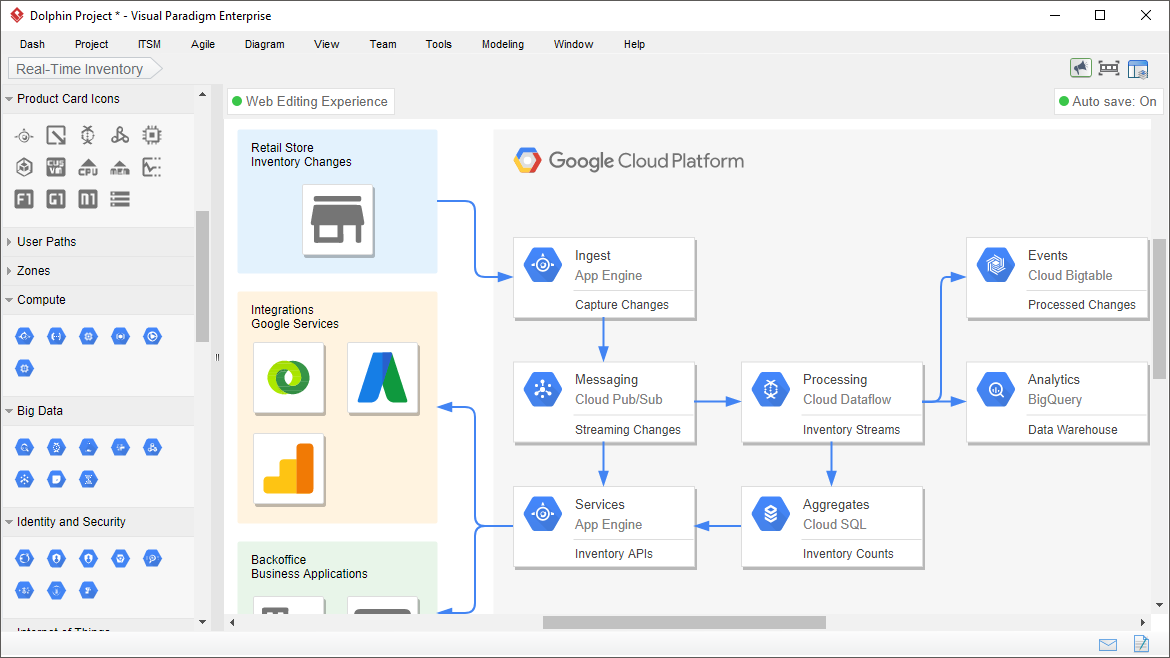
Digital Asset Management and Sharing
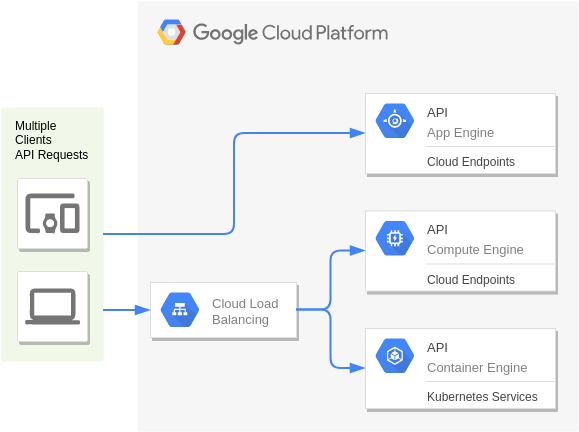
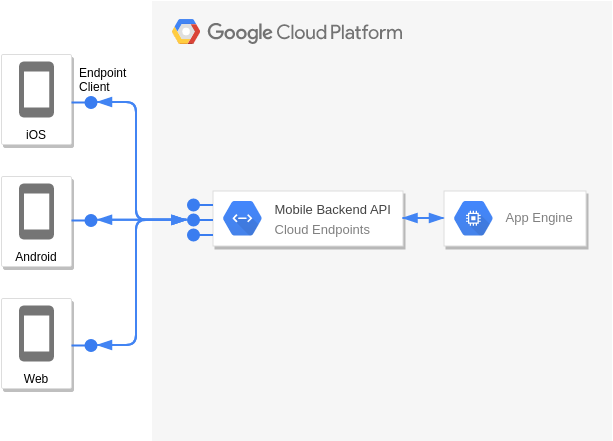
App Engine and Cloud Endpoints
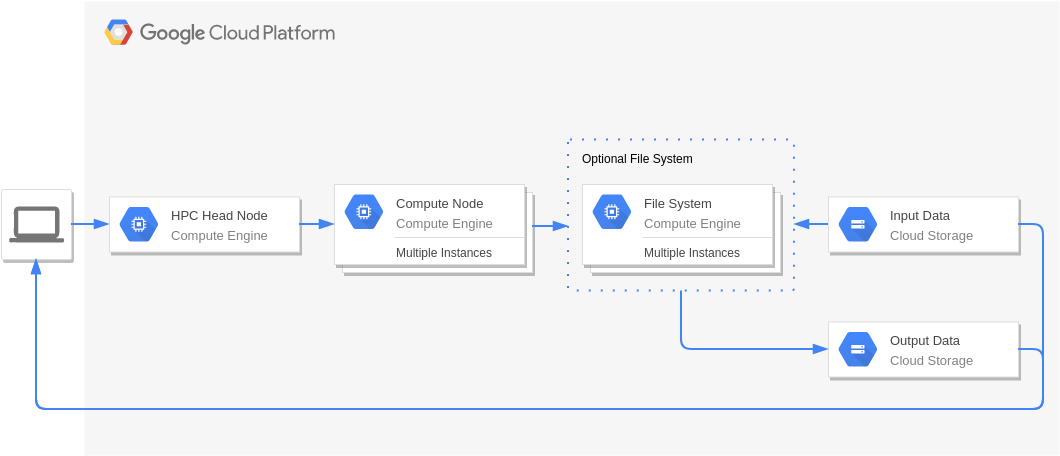
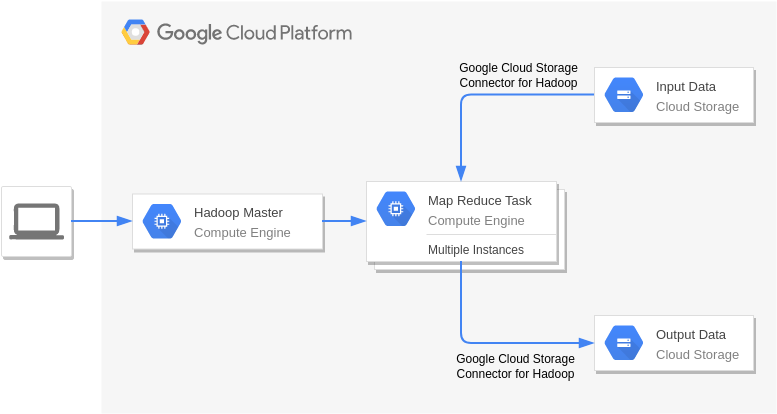
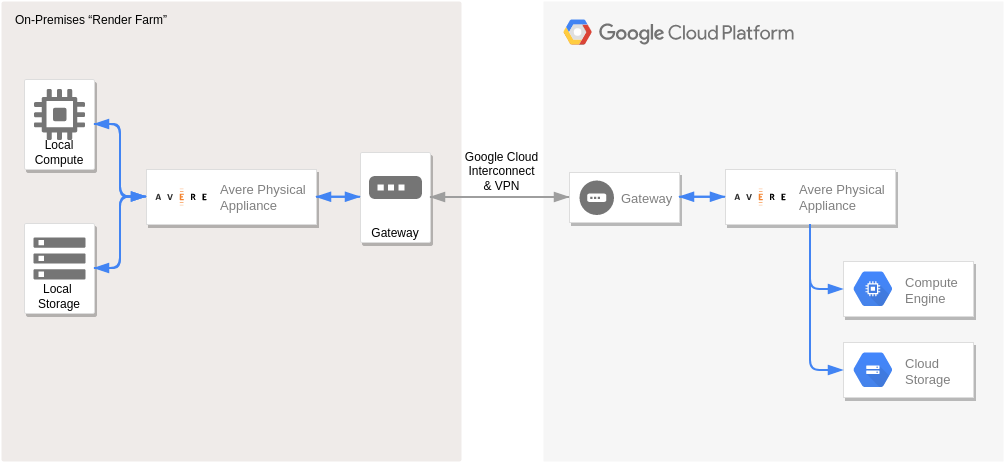
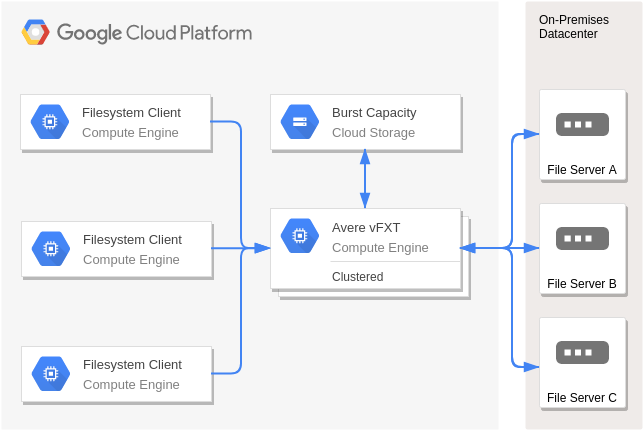
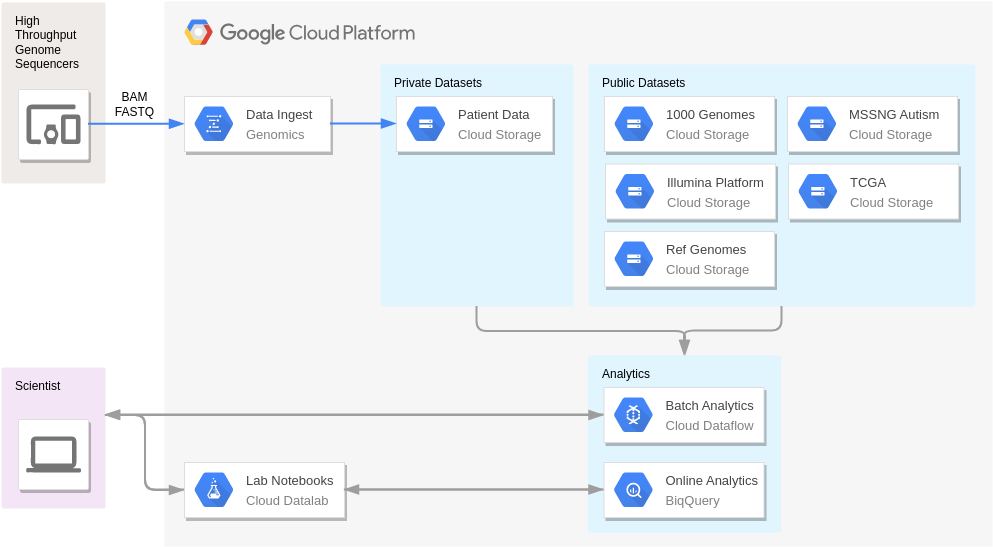
Handoop on Google Cloud Platform
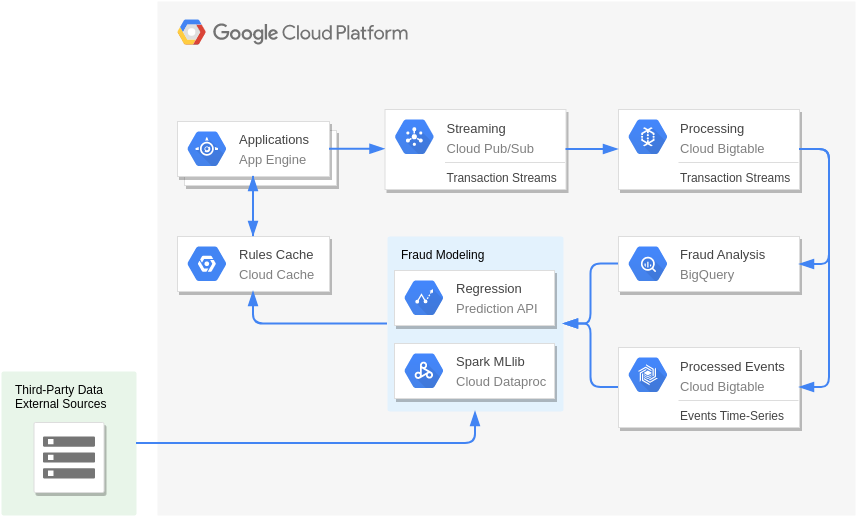
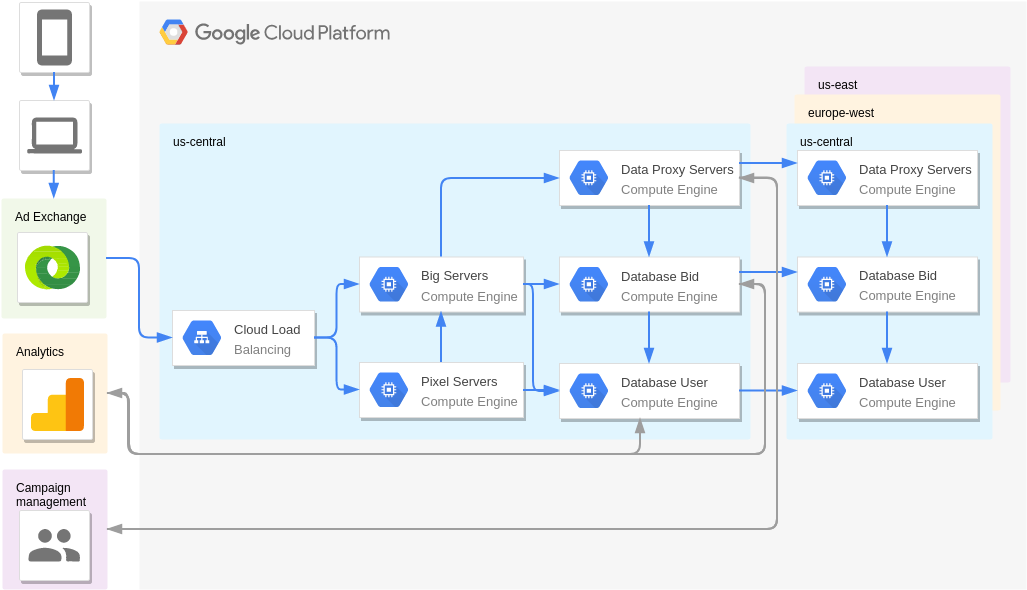
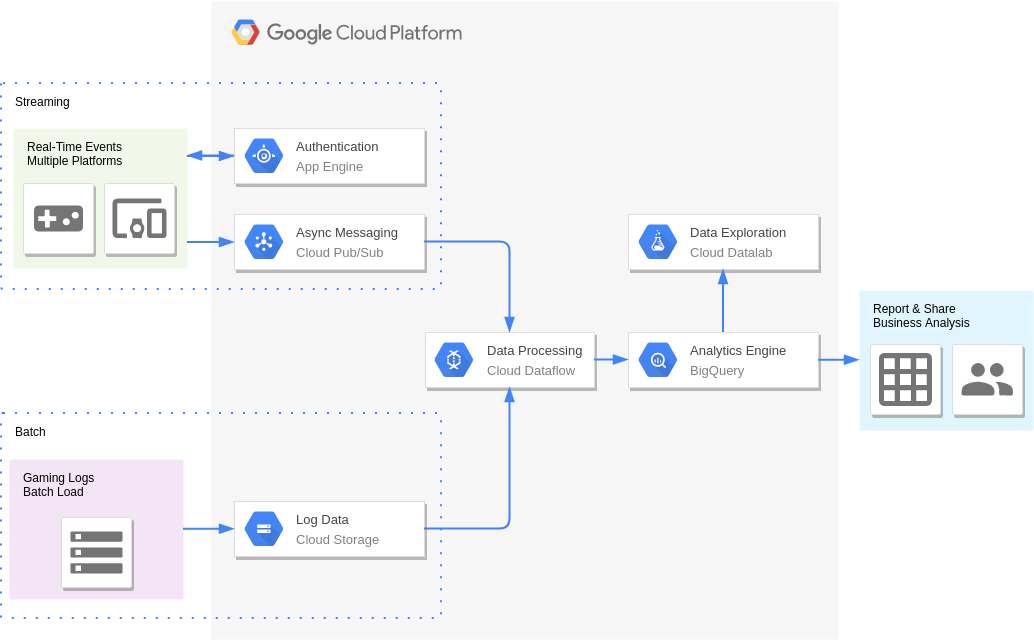
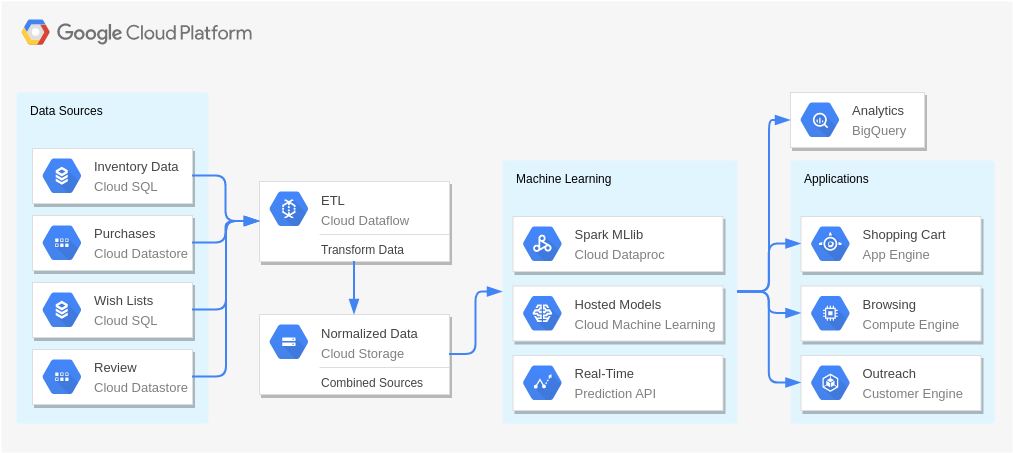
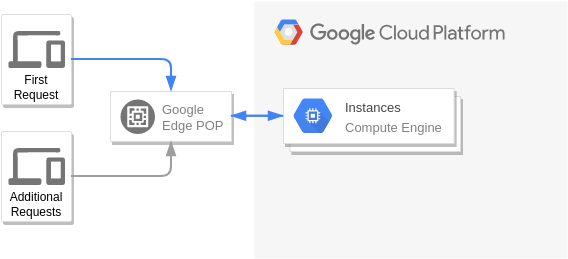
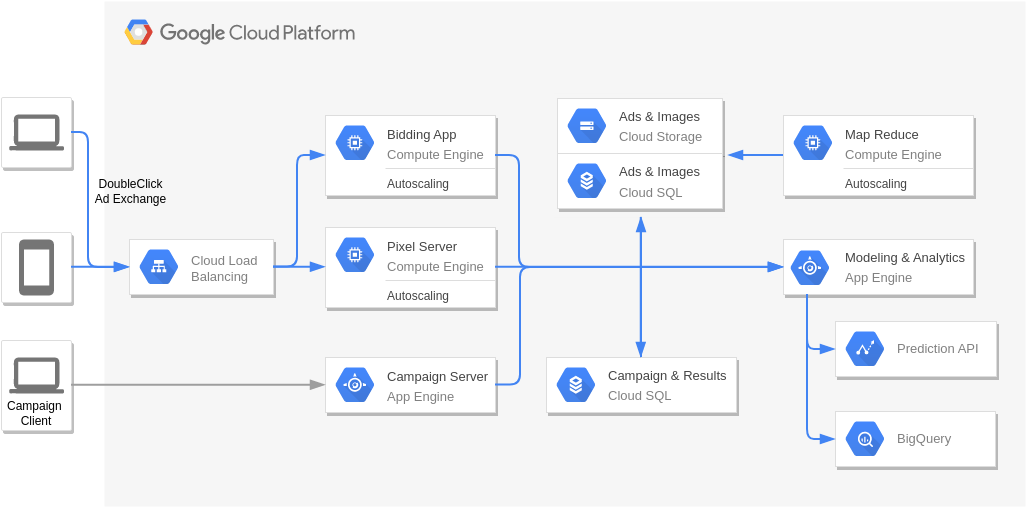
Real-Time Bidding (Digital Marketing)
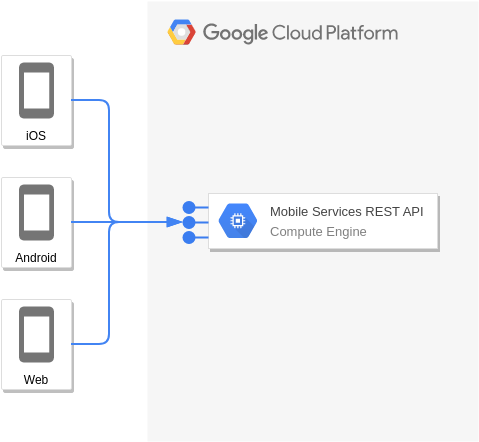
Compute Engine and REST or gRPC
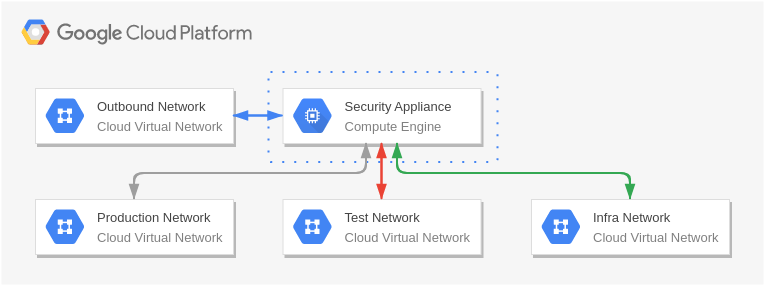
Disaster Recovery Cold standby server
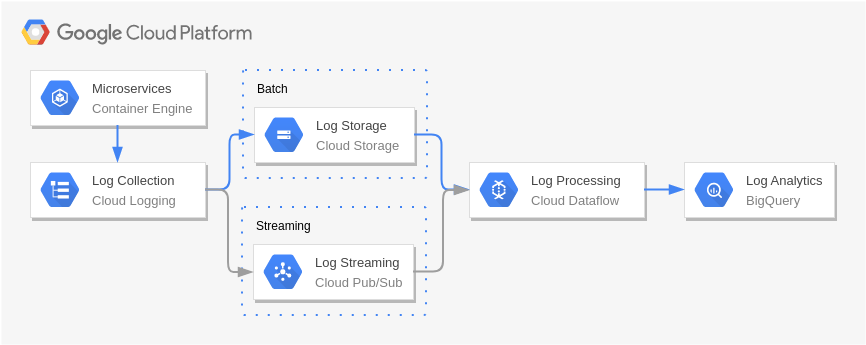
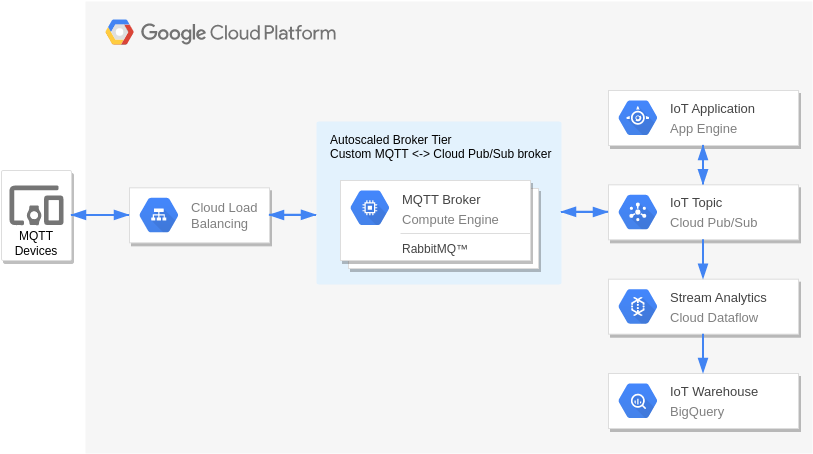
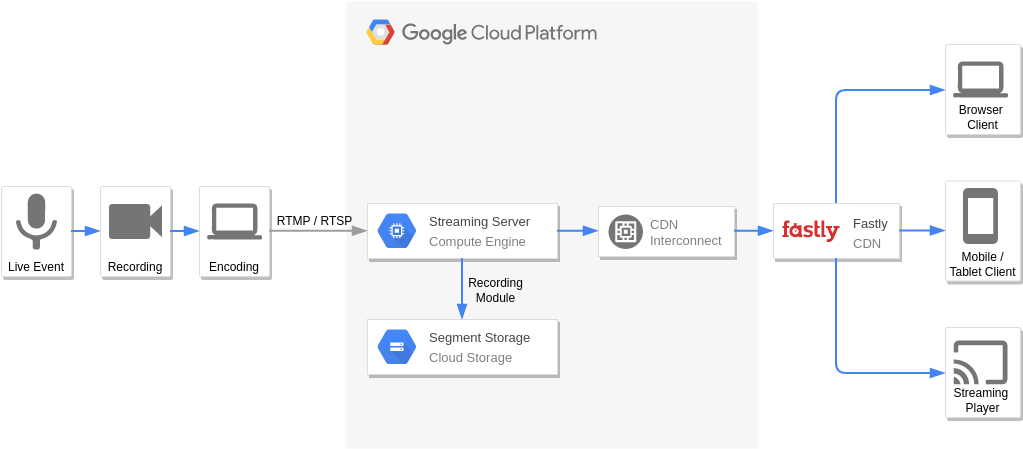
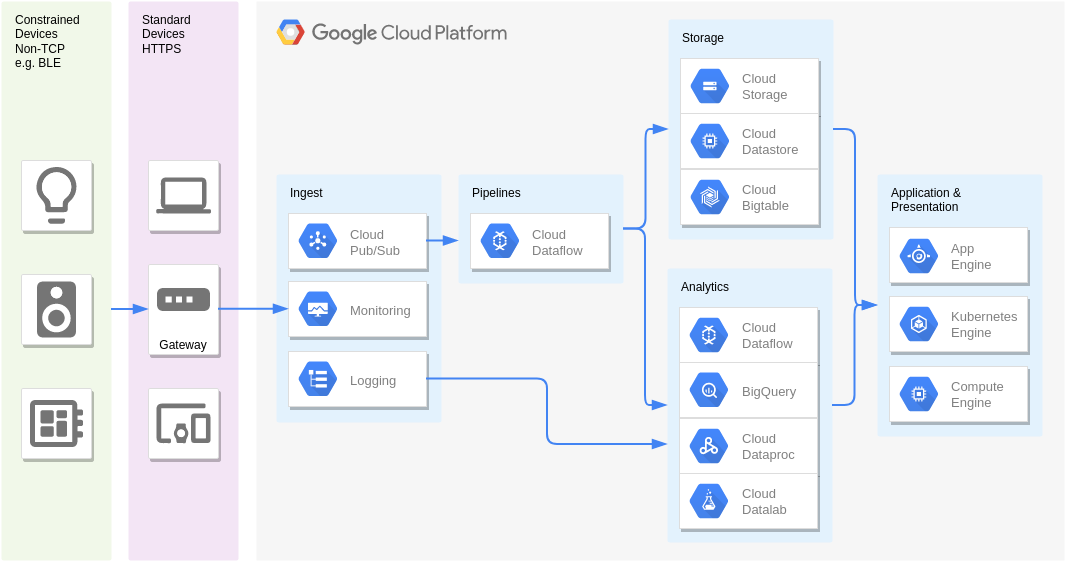
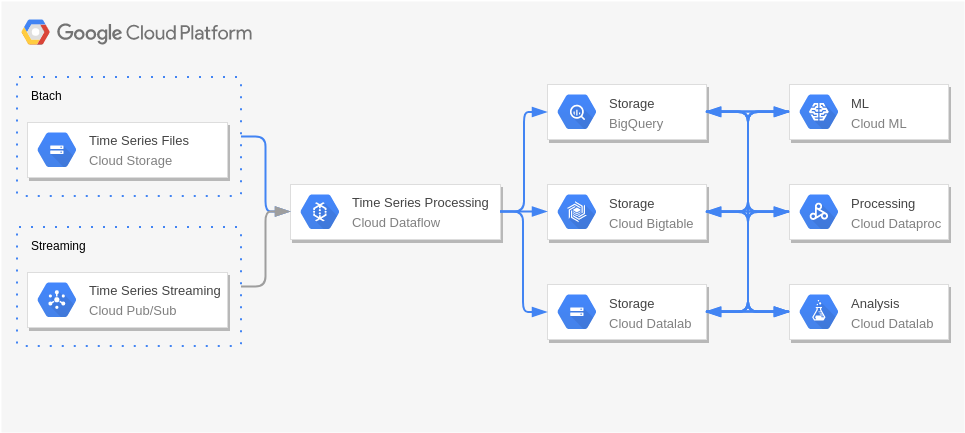
Real Time Stream Processing – Internet of Things
Disaster Recovery Warm static site
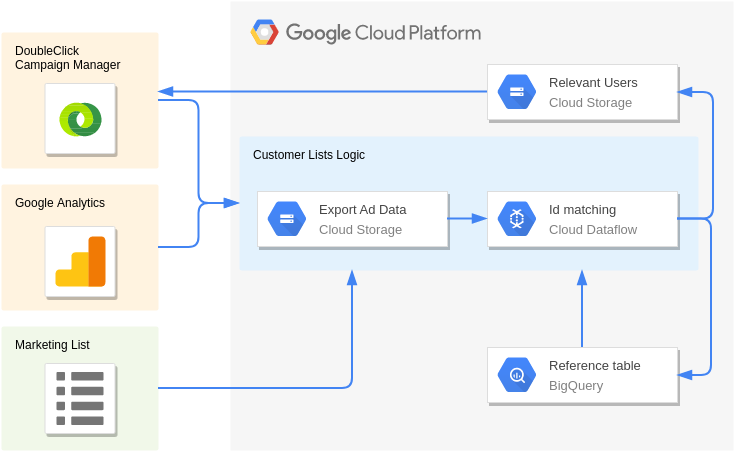
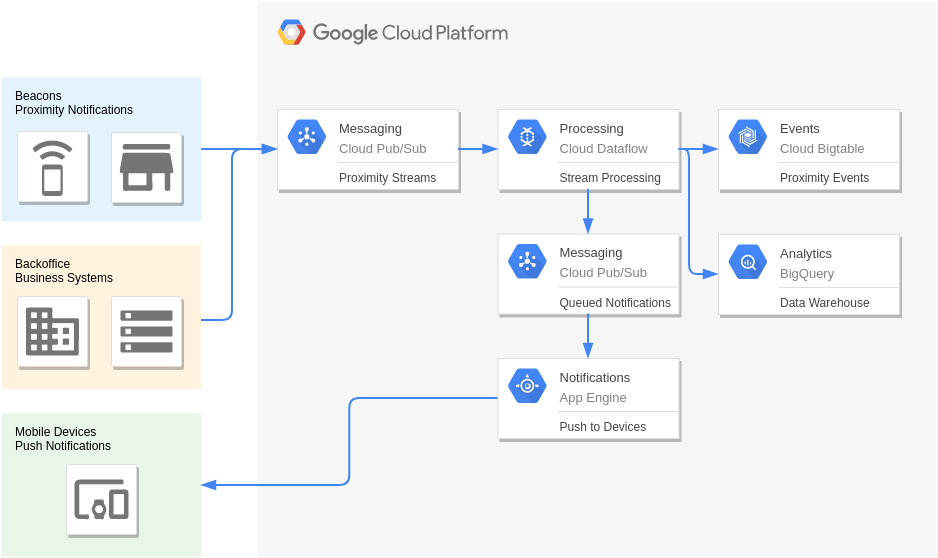
Beacons and Targeted Marketing
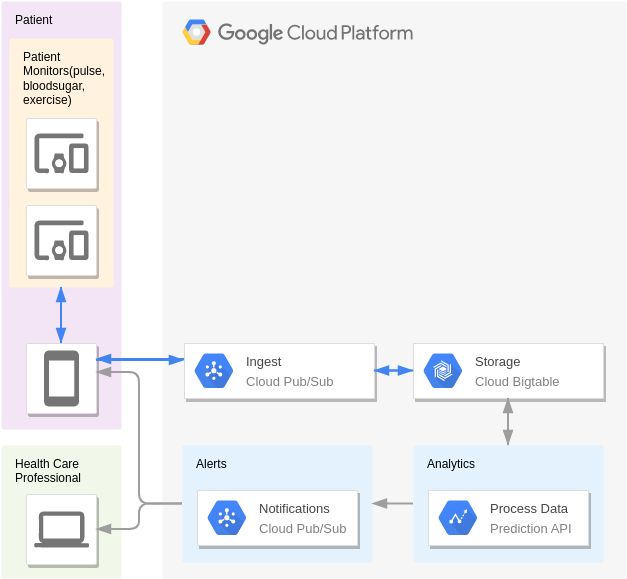
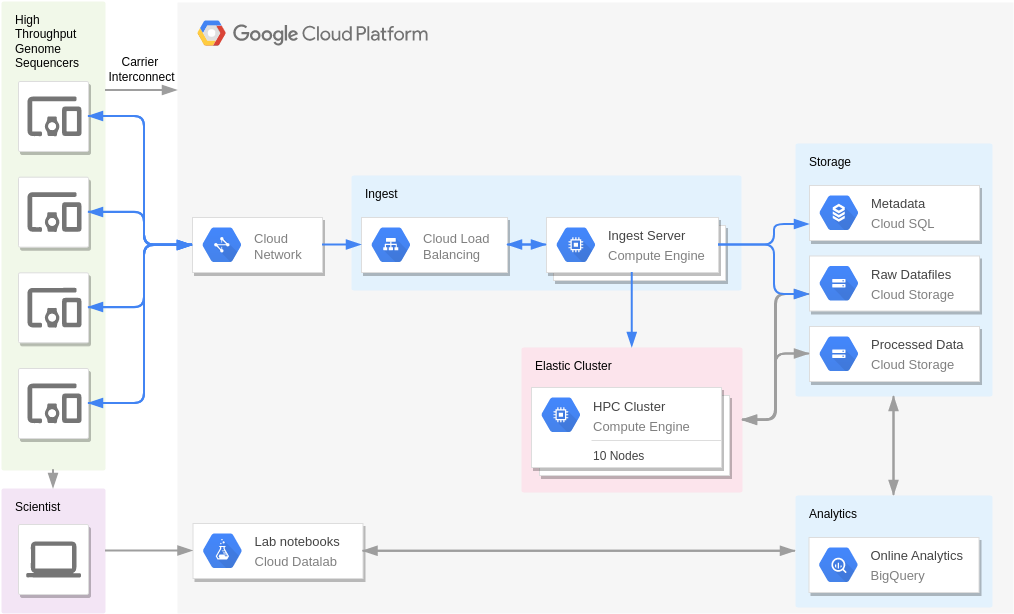
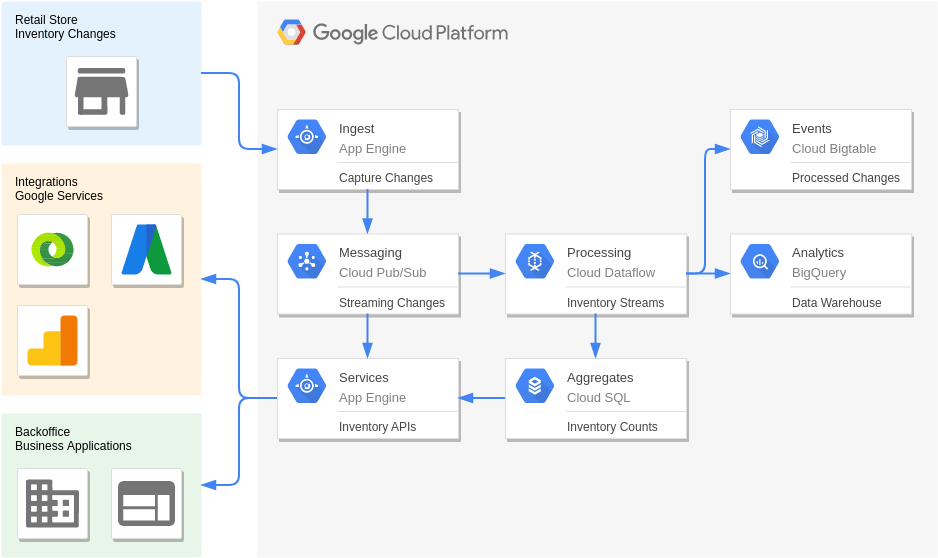
Sensor stream ingest and processing
Conclusion
The Google Cloud Platform Diagram serves as a visual aid to demystify the intricate web of services and resources within GCP. It is a dynamic representation that evolves with the platform’s continuous enhancements. As businesses embark on their cloud journey, understanding this diagram becomes a crucial step towards harnessing the full potential of Google Cloud Platform. With its diverse offerings and commitment to innovation, GCP remains a frontrunner in the realm of cloud computing.
This post is also available in Deutsche, English, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.