The McKinsey 7S Framework – with Related Examples, Templates and Tools
In the 1970s and 1980s, Americans were suffering from recession and unemployment while trying to find the right way to develop and revitalize their own companies after fully understanding the art of successful Japanese companies. Thomas J. Peters and Robert H. Waterman were long-time employees of the famous McKinsey & Company. They interviewed 62 of the best and oldest large companies in the United States and selected 43 based on the criteria of profitability and growth rate. They selected 43 outstanding model companies, including IBM, Texas Instruments, Hewlett-Packard, McDonald’s, Kodak, DuPont, and other industry leaders, and invented the 7S model.
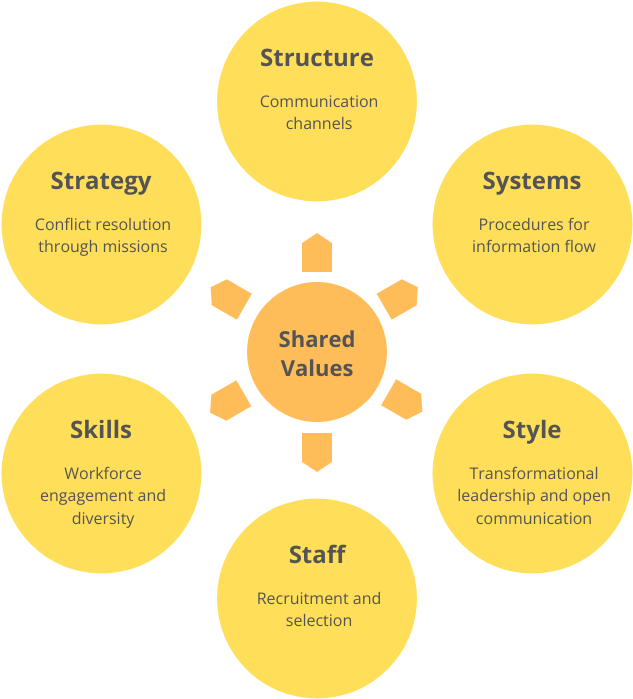
The 7-S model states that all aspects of a company must be considered holistically in the development process. It includes structure, systems, style, staff, skills, strategy and shared values. In other words, it is not enough for a company to have a clear strategy and a well-thought-out action plan, because companies can also make mistakes in the process of implementing their strategies. This is because strategy is only one factor.
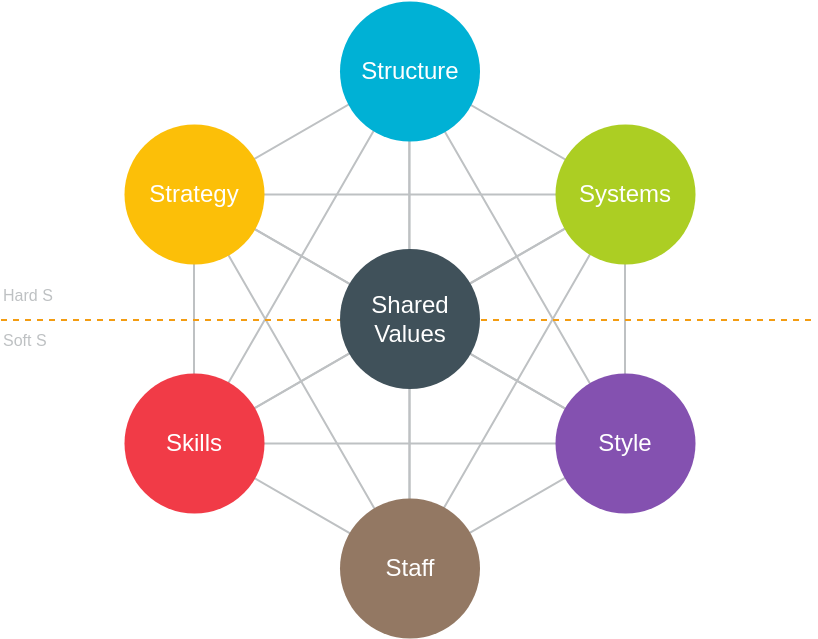
In the model, strategy, structure and systems are considered the “hardware / hard skills” for business success, while style, staff, skills and shared values are considered the “software / soft skills” for successful business operations. Both hardware and software are equally important in how a company wants to succeed, and cannot be paranoid.
What is the 7-S model?
By looking at each of these 7 areas and how they are interconnected, a company can determine if it has the capacity to achieve its goals and how it will respond and adapt to change. The idea is that if one area is lacking or needs to be adjusted, then the other elements need to be adjusted as well. All elements are interconnected, so a change in the performance of any one component will affect another.
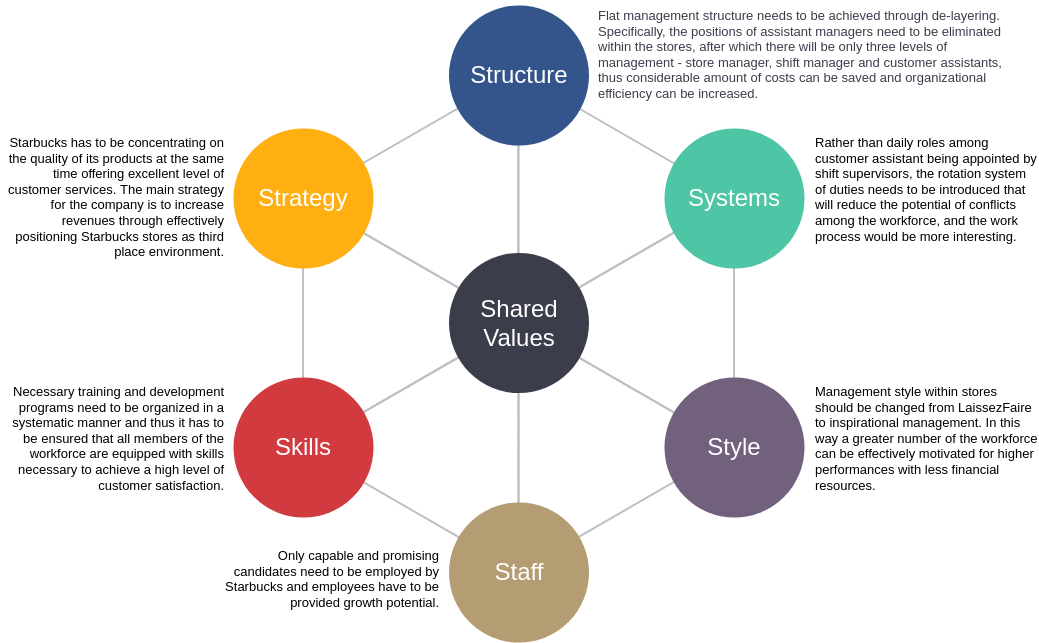
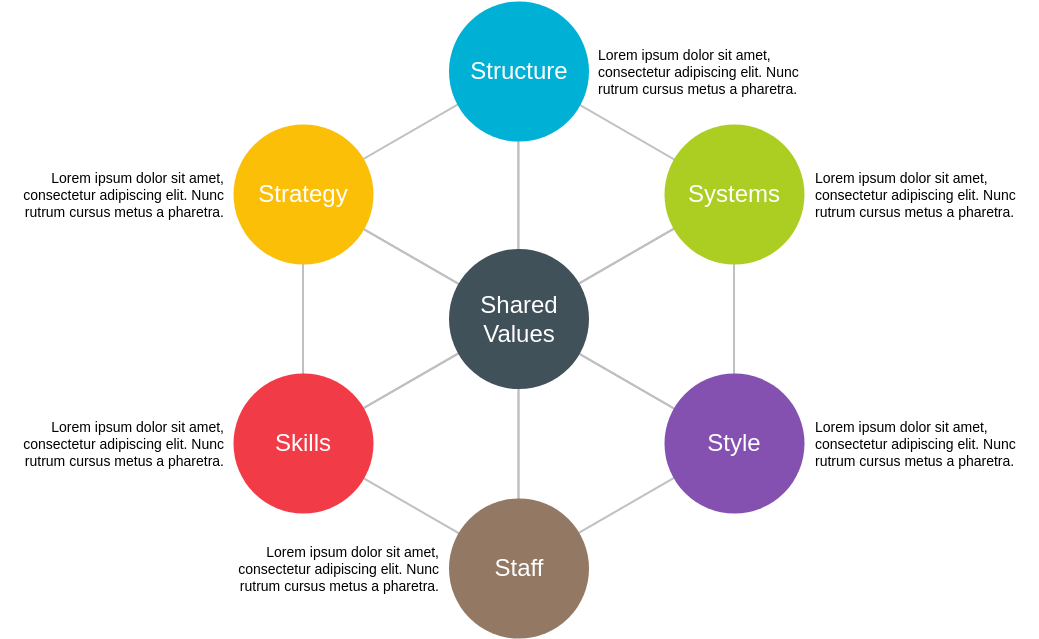
- Strategy: The overall planning of an enterprise for long-term survival and development in the face of rapidly changing business environment.
- Structure: Organizational structure is a model that expresses the arrangement, spatial location, contact and gathering status of all parts of the organization, in order to effectively bring all parts of the organization together to work towards a common goal.
- System: Enterprise system refers to a series of regulations and constraints made on the microstructure and related systems of the enterprise, which is specifically expressed as the standardization and institutionalization of a series of behaviors such as enterprise organization, operation and management.
- Style: It mainly refers to the corporate culture, which is the sum of the values, professional ethics and behavioral norms formed by the enterprise in the long-term production and operation process and commonly recognized and followed by all employees.
- Staff: the knowledge and skills of employees.
- Skills: All production and management activities of the enterprise are carried out by employees with certain technical abilities using the corresponding factors of production to realize the process of creating material and spiritual wealth.
- Shared values: It is the strategy of all members of the organization. The common understanding of the goals and objectives of the enterprise is the basic view of the meaning of existence, business indicators and other issues, as well as the criteria for judging the behavior of enterprises and employees. Shared values are the core of corporate culture
As shown in the figure below: Shared values are at the center and will drive and promote other elements. When the shared values change, it will bring about changes in other elements.
How does the 7S model work?
The model is based on the idea that for a business to operate well, the seven factors need to work together and interact with each other. Assuming you are at point A and your goal is point B, you can use this model to analyze the gap between A and B and how these seven factors need to be aligned to reach your goal. As simple as it sounds, these seven elements only give you a perspective to think about, but the real answer to the question must rely on your skills, expertise and experience.
Edit this McKinsey 7S Model Template
When you consider applying the McKinsey 7S model, you may want to start with the following.
- First look at the shared values of your business: do they match your organizational structure, strategy, and systems? If not, what changes need to be made?
- Look at the “hardware” elements: How do they support each other and interact with each other? What needs to be changed? (It may be helpful to brainstorm using questions from each of the following areas)
- Look at the “software” factors: do they support the “hardware” factors? Do they match each other? What needs to be changed? (It may be helpful to brainstorm using questions from each of the following areas)
- After you have made adjustments to the seven factors, you need to analyze again whether the adjustments are justified? Of course, it will also take some time to wait for the implementation results.
structure
- How are our corporate teams divided?
- What is the organizational structure?
- How do the different departments work together?
- How do team members work with each other?
- Is decision-making centralized or decentralized? Is this type of decision making necessary?
- Is communication direct or indirect?
systems
- What are our corporate systems?
- Where is control centralized? What are the appraisal and evaluation systems?
- What are the internal rules and processes of the team?
style
- What is the management style of the company?
- Is leadership effective?
- Do team members tend to be competitive or supportive?
skills
- What are the company’s strongest technologies?
- Are there any technical gaps?
- What are the company’s core competencies?
- Does the current workforce have the right skills for their current position?
- How are these skills measured?
strategy
- What is our strategy?
- How do we achieve our goals?
- How do we face competitive pressures?
- What are the changes in customer needs? How do we deal with it?
- What changes to our strategy are required by the external environment?
- What are the core values?
- What is the team culture?
- How strong are the values?
- What are the fundamental values on which the company was founded?
This post is also available in Deutsche, Español, فارسی, Français, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.