BPMN Pools and Lanes: A Guide to Effective Process Modeling
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical notation for modeling business processes, which is widely adopted by organizations to model, analyze, and communicate their business processes. It provides a standardized approach for modeling the flow of activities within a business process, making it easier for all stakeholders to understand the process and collaborate in its improvement.
In BPMN, a pool represents a participant in a business process, while a lane represents a functional decomposition within a participant. Understanding the differences between pools and lanes is essential for effectively modeling business processes using BPMN.
What is a Pool?
A pool is a visual representation of a participant in a business process, such as a department, a company, or a system. Pools are used to define the scope of a business process, and they can contain one or more lanes, which represent functional decompositions within the participant.
For example, a pool could represent a company, and its lanes could represent the different departments within the company, such as sales, marketing, and finance.
What is a Lane?
Lanes are used to divide the flow of activities within a pool into different functional areas. They provide a clear understanding of the roles and responsibilities of each functional area in the process, making it easier to understand who is responsible for each task in the process.
For example, in a sales process, the sales lane could represent the tasks performed by the sales department, such as lead generation and order processing, while the marketing lane could represent the tasks performed by the marketing department, such as marketing campaign planning and execution.
It is important to note that pools and lanes are not equivalent to participants and activities in a business process. A participant can contain multiple lanes, and an activity can belong to multiple lanes. This allows for a more detailed and accurate representation of a business process.
When to Use Pools and Lanes
Pools and lanes are used in different scenarios, depending on the needs of the business process being modeled.
Pools are used to define the scope of a business process, and to represent the different participants involved in the process. When modeling a business process that involves multiple participants, such as a process that involves multiple departments within a company or multiple companies, pools should be used to define the scope of the process and to represent each participant.
Lanes are used to represent functional decompositions within a participant. When modeling a business process that involves multiple functional areas within a participant, lanes should be used to represent each functional area and to show the tasks performed by each area.
For example, in a sales process, a pool could represent the company, and its lanes could represent the sales and marketing departments. In this scenario, the sales lane would show the tasks performed by the sales department, such as lead generation and order processing, while the marketing lane would show the tasks performed by the marketing department, such as marketing campaign planning and execution.
How To Add A Lane To A BPMN Pool
In a business process diagram, we can first add a pool in our diagram.
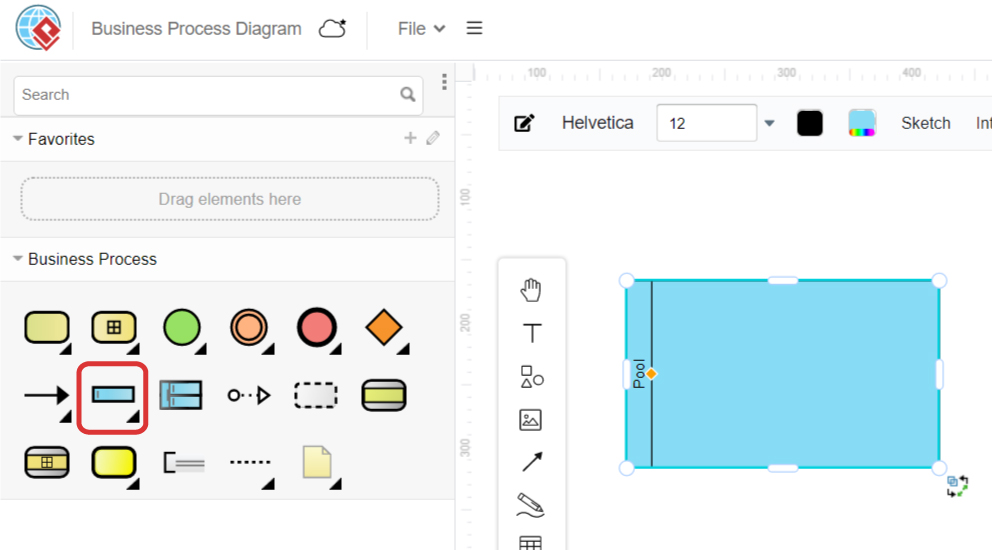
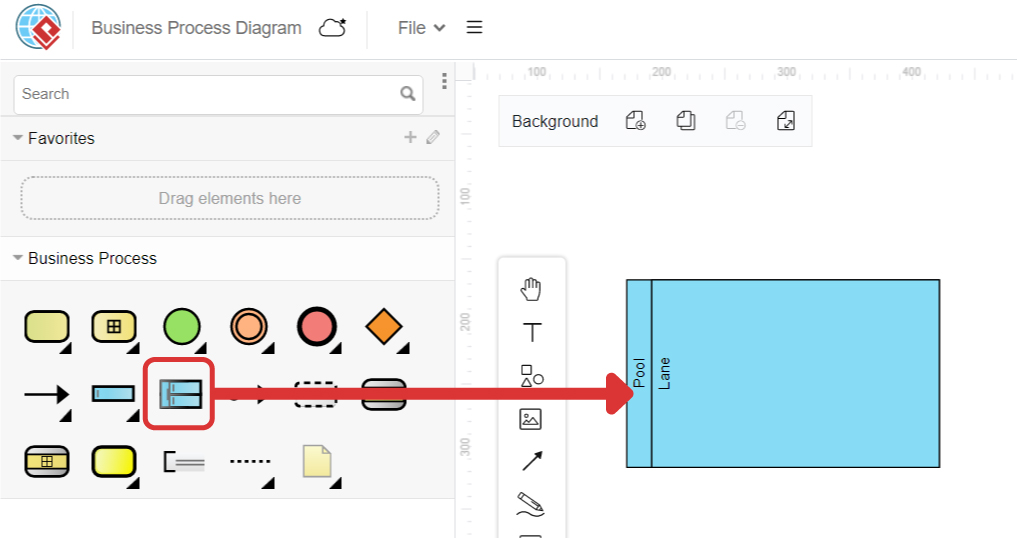
Select the lane tool in the diagram panel, then click the pool on the editor.
We can see that a lane is then created inside the pool.
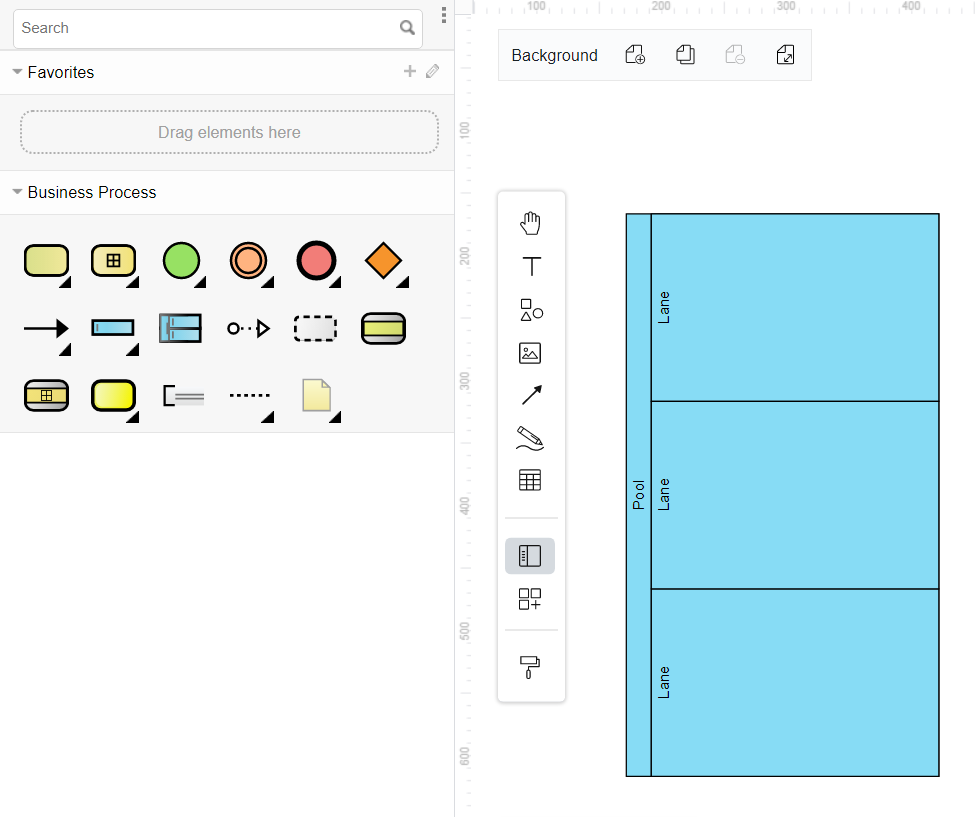
In case we want to create more than one lane, we can repeat the above steps to create more lanes in the same pool.
Conclusion
Pools and lanes are essential elements in BPMN for modeling business processes. Pools are used to define the scope of a business process and to represent the different participants involved in the process, while lanes are used to represent functional decompositions within a participant.

