Comprehensive BPMN Diagram Tutorial
Introduction
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical notation used to represent business processes in a clear and understandable manner. BPMN diagrams are widely used in business process modeling, analysis, and documentation. In this tutorial, we will explore the purpose, key concepts, and elements of BPMN diagrams and learn by examples using pre-made templates in Visual Paradigm Online.
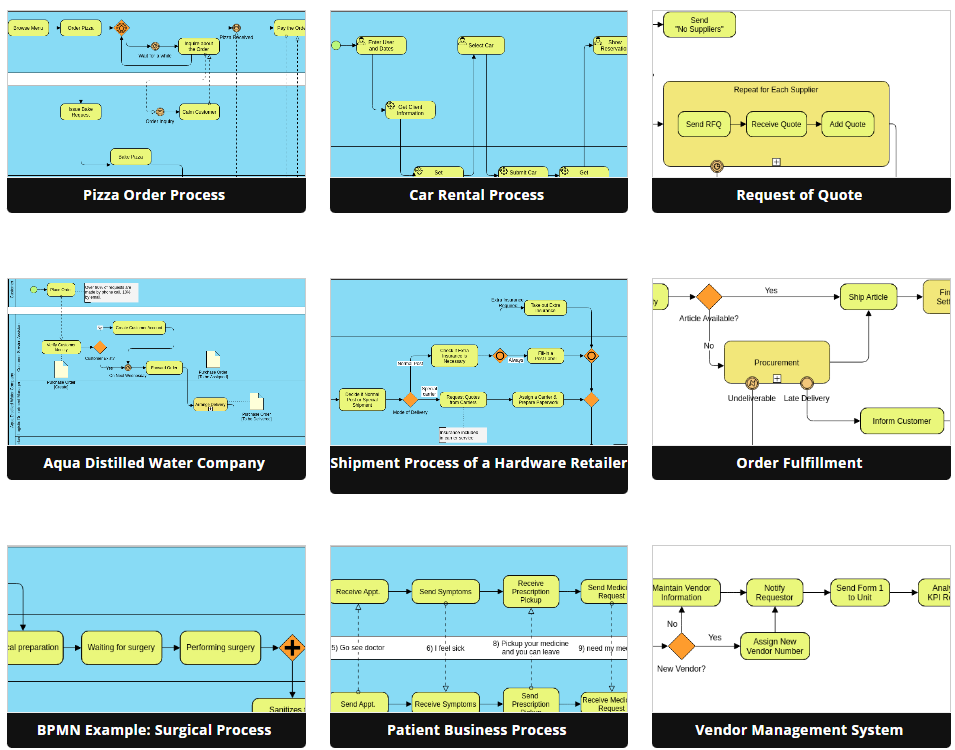
1. Introduction to BPMN
What is BPMN?
BPMN, or Business Process Model and Notation, is a visual language for representing business processes. It provides a standardized way to graphically depict processes, making them easier to understand and communicate across different teams and stakeholders. BPMN diagrams are commonly used in business process analysis, improvement, and automation.
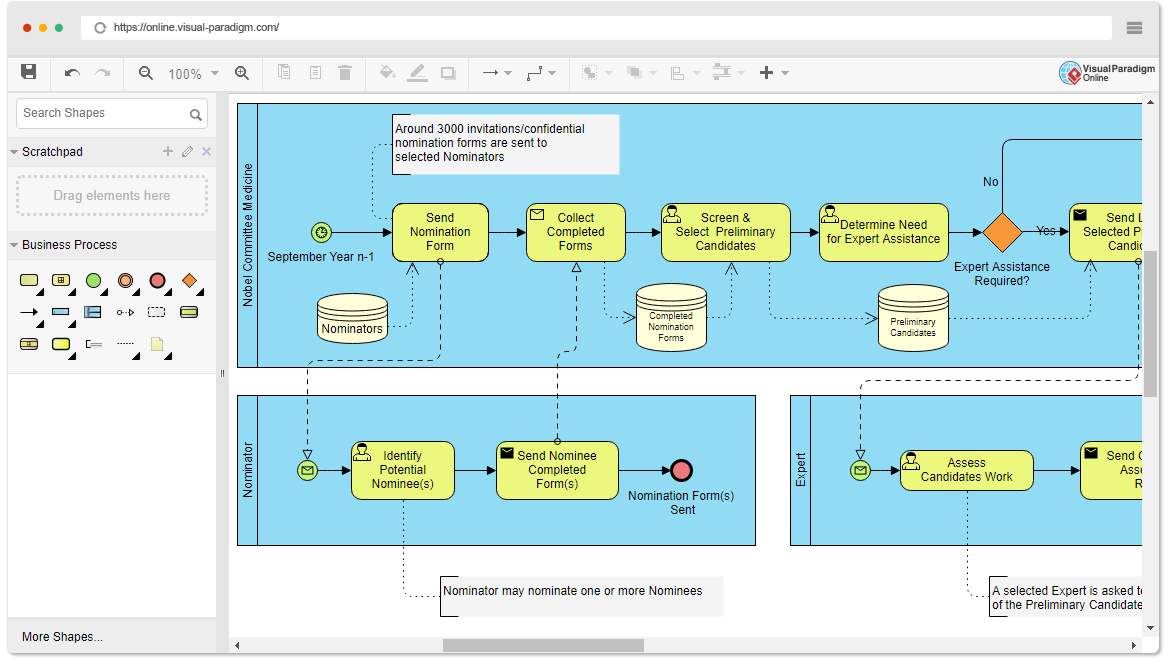
Why Use BPMN?
- Clarity: BPMN diagrams use standardized symbols and notation, making them easy to understand by both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Communication: They facilitate effective communication between business analysts, process designers, and developers.
- Process Improvement: BPMN helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for process improvement.
- Automation: BPMN diagrams can be used as a basis for automating business processes using BPM (Business Process Management) software.
2. Key Concepts in BPMN
Process
A BPMN diagram represents a business process. A process is a collection of related activities that transform inputs into outputs to achieve a specific business goal.
Activities
Activities are tasks or work steps within a process. They can be of two types:
- Task: Represents an individual work item or action.
- Sub-process: Represents a subprocess, which is a higher-level process with its own set of activities.
Flow Objects
Flow objects define the flow of a process. Key flow objects include:
- Sequence Flow: Represents the order in which activities are performed.
- Gateway: Decides which path to follow based on conditions.
- Event: Represents something that happens during the process, such as the start, end, or intermediate events.
Connectors
Connectors (sequence flows) link flow objects, defining the order of execution.
Swimlanes
Swimlanes are used to organize activities and show who is responsible for each task. They can be divided into pools (for organizations) and lanes (for specific roles or departments).
3. BPMN Elements
Common BPMN Symbols
Here are some common BPMN symbols and their meanings:
- Start Event: Indicates where a process begins.
- End Event: Marks the end of a process or subprocess.
- Task: Represents a manual or automated activity.
- Gateway: Decides the flow direction based on conditions.
- Sequence Flow: Shows the order of execution between activities.
- Message Flow: Represents communication between processes or participants.
- Pool: Organizes processes into separate groups (e.g., organizations).
- Lane: Divides a pool into segments for roles or departments.
4. Creating BPMN Diagrams in Visual Paradigm Online
Visual Paradigm Online is a web-based BPMN diagram tool that simplifies the creation of BPMN diagrams. Here’s how to get started:
- Access Visual Paradigm Online: Go to Visual Paradigm Online.
- Create a New Project: Sign in or create a new account if you don’t have one. Then, create a new project and select “BPMN Diagram” as the diagram type.
- Add Elements: Drag and drop BPMN elements from the toolbar to the canvas. Connect them using sequence flows.
- Customize Elements: Double-click on elements to edit their properties, labels, or other details.
- Organize Using Swimlanes: To use swimlanes, add pools and lanes to the diagram and assign activities to specific lanes.
- Save and Export: Save your diagram in Visual Paradigm Online and export it as an image or PDF.
Conclusion
BPMN diagrams are powerful tools for documenting, analyzing, and optimizing business processes. Visual Paradigm Online simplifies the creation of BPMN diagrams, making it accessible to both business and technical professionals. By following this tutorial and practicing with examples, you can become proficient in creating BPMN diagrams and effectively communicate and improve business processes.
This post is also available in Deutsche, Español, فارسی, Français, English, Bahasa Indonesia, 日本語, Polski, Portuguese, Ру́сский, Việt Nam, 简体中文 and 繁體中文.

















