Comprehensive Guide to Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
Introduction
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model is a widely recognized framework for effectively managing and implementing organizational change. Developed by Dr. John Kotter, a professor at Harvard Business School and a renowned authority on leadership and change, this model provides a structured approach to guide organizations through the complex process of change. This comprehensive guide will delve into the purpose, key concepts, and elements of Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model, along with real-world examples to illustrate its application.
Purpose of Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model:
The primary purpose of Kotter’s model is to help organizations navigate and successfully execute transformative change initiatives. It acknowledges that change is often met with resistance and that a systematic approach is necessary to overcome these challenges. By following these eight steps, organizations can enhance their ability to adapt to new circumstances, improve performance, and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Key Concepts and Elements of Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model:
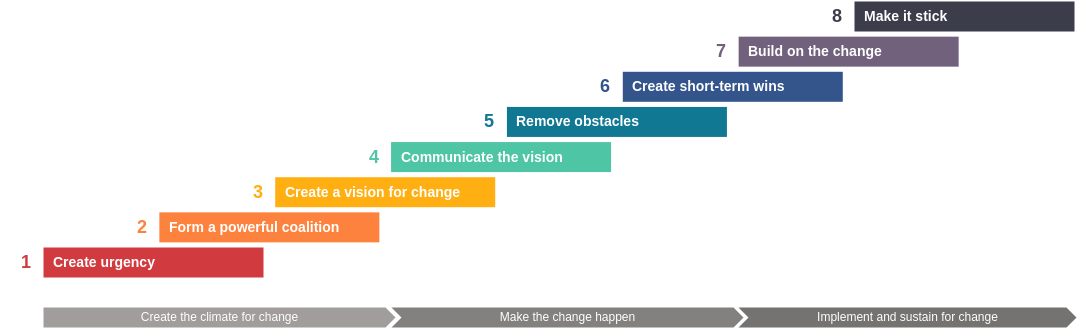
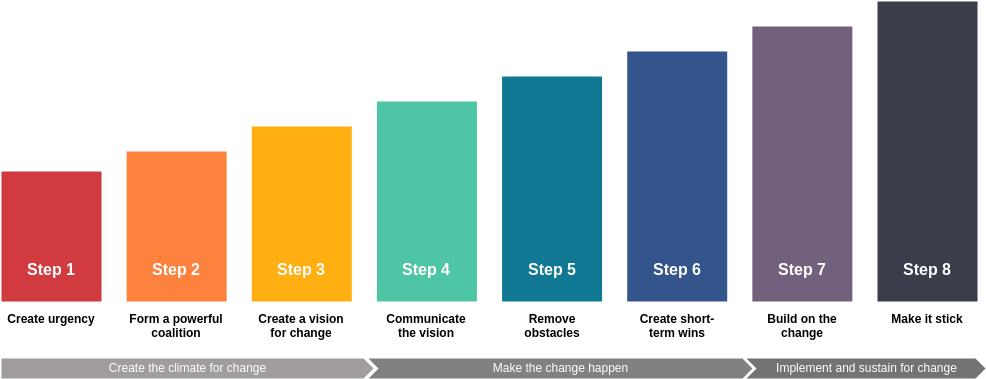
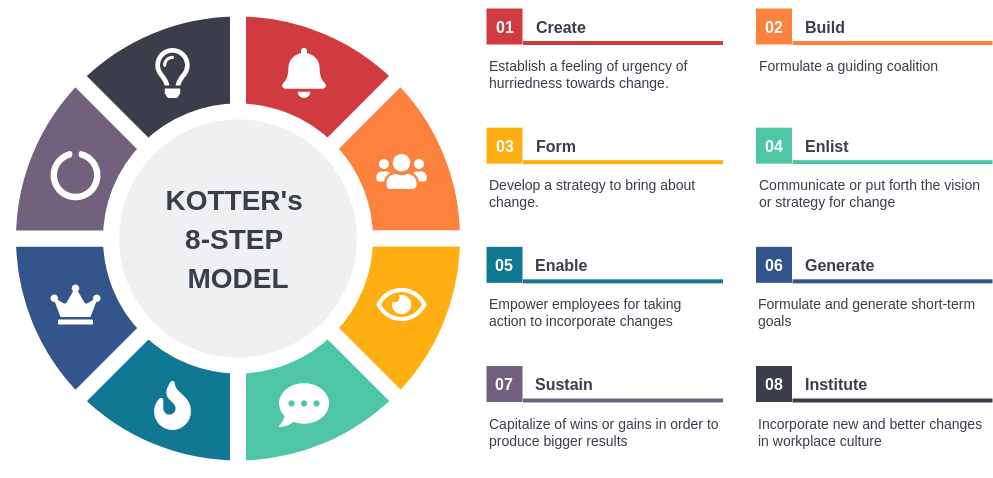
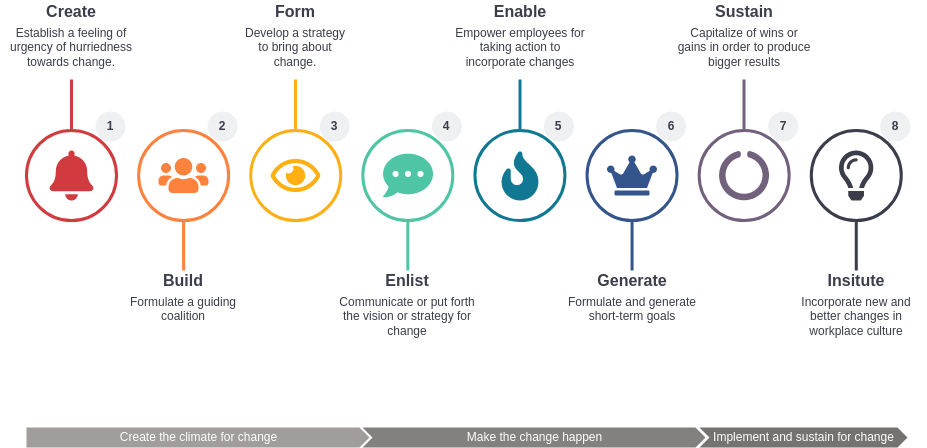
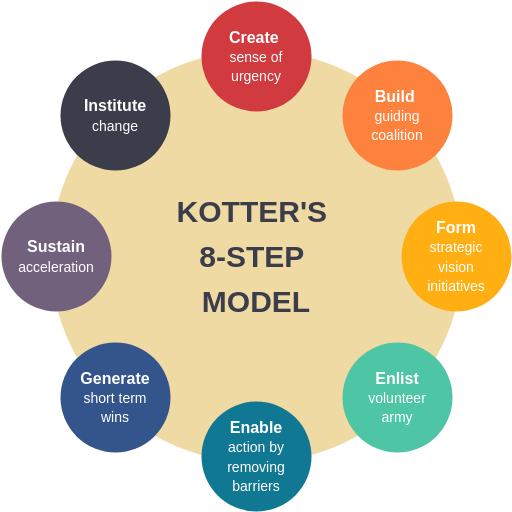
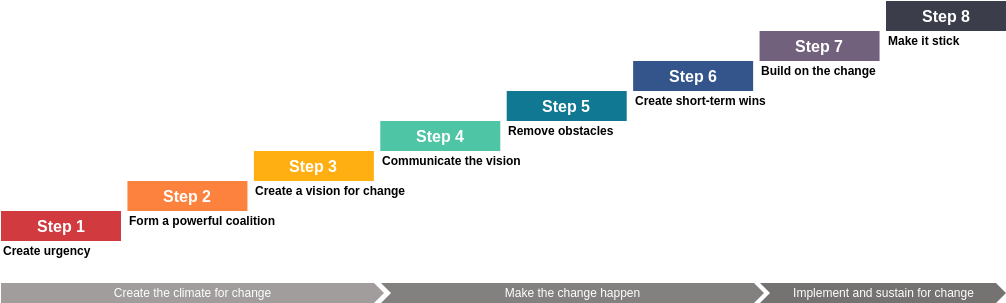
Step 1: Create a Sense of Urgency
Concept: To initiate change effectively, there must be a compelling reason for it. Creating a sense of urgency helps stakeholders understand the need for change and motivates them to take action.
Elements:
- Identify and communicate the reasons behind the change.
- Share data, facts, and stories that illustrate the current challenges.
- Encourage open and honest discussions about the need for change.
Example: Suppose a manufacturing company is facing declining sales due to outdated technology. The leadership team communicates the urgency by presenting market research showing competitors’ advancements and the risk of losing market share.
Step 2: Build a Guiding Coalition
Concept: Change requires strong leadership and support from key individuals across the organization. A guiding coalition is a group of influential leaders who can champion the change effort.
Elements:
- Assemble a diverse team of leaders who can drive change.
- Ensure coalition members are committed to the change and can influence others.
- Define roles and responsibilities within the coalition.
Example: In a healthcare organization, a guiding coalition is formed consisting of senior doctors, nurses, and administrators to lead the implementation of a new electronic health record system.
Step 3: Form a Strategic Vision and Initiatives
Concept: A clear vision provides direction and purpose for the change. Develop a concise vision statement and identify the key initiatives necessary to achieve it.
Elements:
- Craft a vision statement that is easy to understand and inspiring.
- Define specific initiatives and objectives aligned with the vision.
- Communicate the vision and initiatives throughout the organization.
Example: A retail company envisions becoming a leader in sustainable practices. They outline initiatives such as reducing carbon emissions, sourcing eco-friendly products, and promoting recycling.
Step 4: Enlist a Volunteer Army
Concept: Empower employees at all levels to take ownership of the change. Create enthusiasm and commitment by involving as many people as possible.
Elements:
- Identify and recruit change champions from different departments.
- Provide training and resources to these change agents.
- Encourage them to inspire others and lead by example.
Example: A tech startup encourages employees to participate in innovation workshops and offers incentives for proposing and implementing process improvements.
Step 5: Enable Action by Removing Barriers
Concept: Many obstacles can hinder change efforts. Leaders must identify and eliminate these barriers to allow for smooth progress.
Elements:
- Identify obstacles, both structural and cultural, that impede change.
- Empower employees to challenge the status quo and suggest solutions.
- Provide the necessary resources and support to overcome barriers.
Example: An educational institution identifies outdated administrative processes as a barrier to academic innovation. They allocate resources to digitize administrative tasks, making it easier for faculty to focus on teaching.
Step 6: Generate Short-Term Wins
Concept: Celebrate early successes to build momentum and demonstrate that change is achievable. These wins help maintain enthusiasm and support for the long-term transformation.
Elements:
- Identify quick-win opportunities that align with the vision.
- Communicate and celebrate achievements throughout the organization.
- Reinforce the connection between actions and positive outcomes.
Example: A software development team, adopting agile methodologies, delivers a new feature ahead of schedule, resulting in increased user satisfaction and boosting team morale.
Step 7: Sustain Acceleration
Concept: To prevent regression and ensure long-term success, organizations must continue to build on their momentum and incorporate change into the culture.
Elements:
- Embed new behaviors and practices into everyday routines.
- Recognize and reward individuals who embrace the change.
- Continuously evaluate progress and make necessary adjustments.
Example: A financial institution maintains its commitment to customer-centricity by regularly reviewing customer feedback and adapting its services accordingly.
Step 8: Institute Change
Concept: Make the change a permanent part of the organizational culture. Ensure that the new behaviors, processes, and systems are fully integrated.
Elements:
- Incorporate change into policies, procedures, and performance evaluations.
- Develop leadership competencies that support the new culture.
- Continuously communicate the importance of sustaining change.
Example: A pharmaceutical company successfully transitions from a traditional hierarchical structure to a more collaborative, cross-functional approach, with all HR policies and practices aligned with this new way of working.
Real-World Examples:
- General Electric (GE): In the early 2000s, GE faced a need for significant change to adapt to a shifting business landscape. They implemented Kotter’s model to create a sense of urgency around innovation and to build a guiding coalition focused on driving change. GE introduced initiatives like “Ecomagination” to promote sustainable technology and generated short-term wins by launching energy-efficient products. This transformation allowed GE to remain competitive and relevant in the market.
- Ford Motor Company: In 2006, Ford was struggling with financial losses and a decline in market share. CEO Alan Mulally used Kotter’s model to create a sense of urgency, build a guiding coalition, and develop a strategic vision that focused on product innovation. Short-term wins came in the form of successful product launches like the Ford Fusion and the restructuring of the company. This approach helped Ford return to profitability and regain its competitive edge.
- Procter & Gamble (P&G): P&G utilized Kotter’s model to drive a major cultural shift toward innovation and collaboration. They created a sense of urgency by highlighting the need to adapt to changing consumer preferences. P&G built a guiding coalition of top executives and empowered employees to be change agents. Short-term wins included the launch of innovative products like the Swiffer. P&G’s sustained commitment to change led to a more agile and consumer-centric organization.
In conclusion, Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model is a powerful framework for organizations seeking to manage and navigate significant change successfully. By understanding its purpose, key concepts, and elements, and by drawing insights from real-world examples, organizations can effectively implement this model to achieve their desired transformation and maintain long-term competitiveness in an ever-evolving business environment.
Conclusion
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model provides a comprehensive framework for organizations to navigate and implement change successfully. By following these steps and utilizing visual aids and templates available in tools like Visual Paradigm Online, organizations can effectively communicate, plan, and execute change initiatives, ultimately achieving their desired transformation goals while engaging their employees in the process.