Save The Whales Infographic
Table of Contents
hide
The biggest mammal on earth is the whale. They live in the ocean everywhere. These large mammals range from 600-pound sperm whales to giant blue whales, weighing more than 200 tons and growing nearly as long as a regular basketball court, over 100 feet in length. From land-living mammals, whales evolved. As such, whales must breathe oxygen, while they can linger for long periods of time submerged under water.
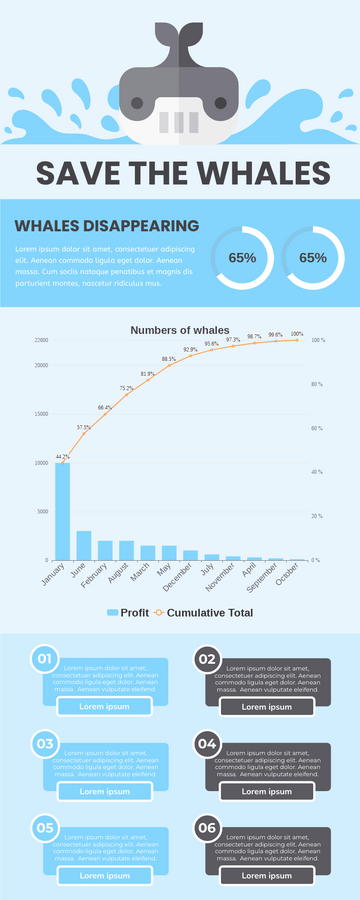
Threats to Whales
Although most populations of whales have been fully protected from hunting for some time, unfortunately, whales and dolphins continue to be threatened by the following factors:
- Ship Collisions – About 90% of accidents occur in collisions with ships or similar vessels.
- Fishing industry – Nets put into the water are non-discriminatory and catch everything from dolphins and whales to sharks, turtles and seals.
- Global warming – causing whales to have trouble. It influences ocean currents, i.e., by making sea water warmer and less salty which reduces food supplies for the whales.
- Pollution – all sort of polluted water, pesticides, paint from vessels, etc. is released in the ocean which makes whales sick and declines in number.
Key Facts of Whales
- Some species of whale such as the sperm whale are able to stay submerged for as much as 90 minutes.
- Whales range in size from the dwarf sperm whale of 2.6 meters and 135 kilograms to the blue whale of 29.9 meters and 190 metric tons, which is the largest known species ever to live.
- Whales feed their infants with their own milk, and take incredibly good care of their young people and teach them life lessons. Whales are social, air-breathing animals.