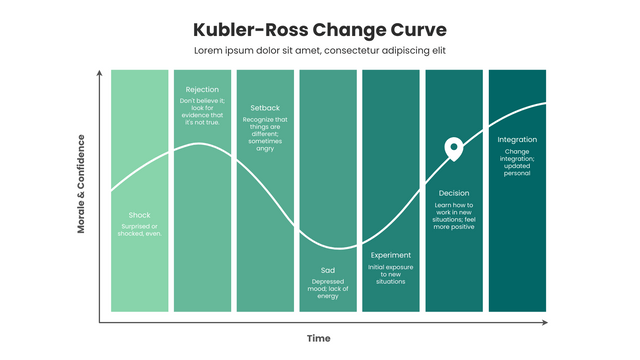
What is The Kubler-Ross Change Curve?
Kübler-Ross, an American psychologist, categorized the psychological reactions and behavioral changes of terminally ill patients from the time they are told of their illness to the time of death into five typical stages: denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance.
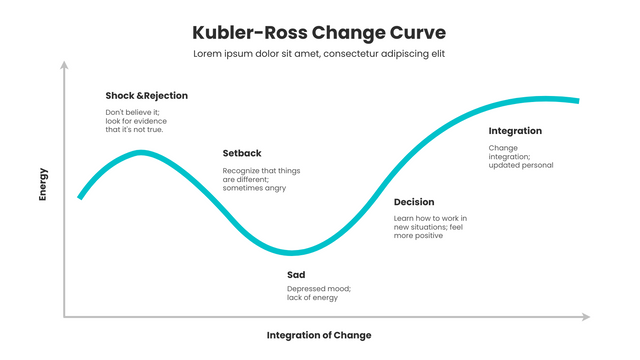
Edit this Kubler-Ross Change Curve Template
This curve model not only started with people’s attitudes toward death, but later extended to life and business; it also developed the ADKAR Organizational Change Model and the John Kotter Change Management Model in eight steps.
The five stages of the Kübler-Ross model include.
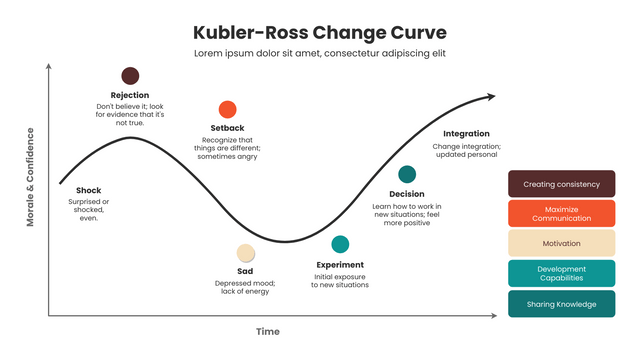
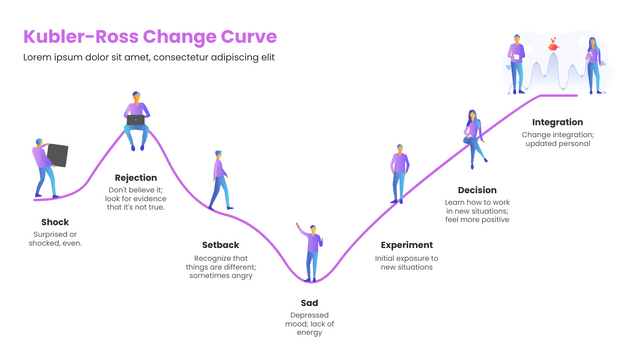
- “Shock & Denial” No way, this can’t be!” “Hasn’t it always been fine?” – Shock or denial is the first and often the shortest step of the curve to experience. At the moment of hearing bad news, people’s defense mechanisms kick in and their brains refuse to accept reality and don’t believe the news is true. Some people even miss the past for a long time and are unable to stop themselves.
- “Anger” Why me? It’s not fair!” “Who can I blame?” – When people finally accept the reality and realize the seriousness of the problem, they begin to become angry. This anger can take many forms; some people will blame themselves and place all the blame on themselves; others will take out their anger on others or on society as a whole. In short, people at this stage will become irritable and cynical.
- “Bargaining” Just let me live to see my son graduate. Please (thou), give me a few more years!” “I’d do anything if she’d wake up.” – After feeling angry, people try to find ways to stop bad things from happening, or try to find a compromise.
- “Depression“” Ugh, why do all this? I’m going to die anyway.” “I don’t want to live, what’s the point of living.” – In this stage of depression, people feel sadness, fear, regret, remorse, or other negative emotions. They may have completely given up the struggle and feel that the future is dark. During this stage, people usually show signs of indifference to the outside world, reject others, and lose all interest in life.
- “Acceptance” “Fine! Since I can’t change this thing anymore, I’ll prepare for the afterlife!” – When people find that wallowing in grief does not help change the facts, they will instead begin to accept the facts and start looking to the future.
Kübler-Ross applies this model to all catastrophic personal losses (job, income, freedom), but also to the loss of family members and even divorce. She also suggests that the stages do not necessarily occur in a specific order and that the patient may not go through all of them, but she believes the patient will go through at least two of them.
Kubler-Ross Change Curve – An Life Example
One weekday, you wake up with a jolt and realize that you are late. You hurriedly wash up and get ready to drive to work, but you find that the car won’t start. As a result, your mental activity will go through the following changes.
1. Shock or denial
Faced with the fact that you are already late for work but your car won’t start, obviously adding insult to injury, shock and denial are surely the first reactions of mental activity. You start to disbelieve how this unlucky thing can happen to you, and then fire the car over and over again to try to get it started.
2. Anger
When you try dozens of times and find that nothing helps, you start to feel angry about your predicament.
3. Bargaining
You start praying for a miracle, hoping that the car will understand your predicament and start up. And promise yourself that you will take good care of your car after today to avoid something like this from happening.
4、Depression
All the negative emotions come to your mind at once and you feel helpless all of a sudden. You worry that your boss will have a problem with your tardiness and even fire you for it.
5. Acceptance
You calm down and know what you should do next. You hastily call an express car on the drop and think about how to fix it in the car.
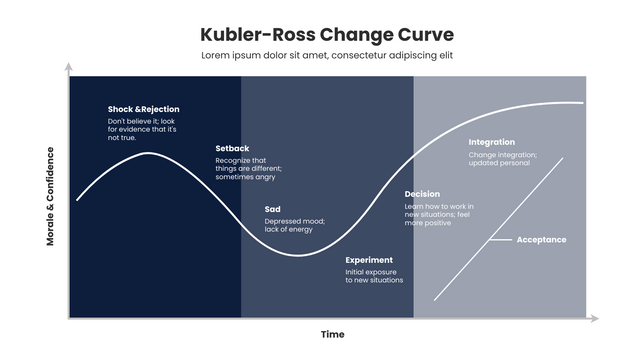
An Updated Kubler-Ross Change Curve
Kubler-Ross proposes that a terminally ill patient goes through five stages of grief after learning of his or her condition. She further proposed that this model could be applied to any dramatic life change situation.
The first five stages of shock & denial, anger, bargaining, depression and acceptance – have been adjusted over the years. There are many versions of the curve that exist. Most of them, however, are consistent in their use of the following basic emotions, which are often grouped into three distinct transitional stages.
- Stage 1 – Shock and denial
- Stage 2 –Anger and depression
- Stage 3 –Acceptance and integration
Edit this Kubler-Ross Change Curve Template
Kubler-Ross Change Curve Templates and Examples
Edit this Kubler-Ross Change Curve Template
Edit this Kubler-Ross Change Curve Template