Home » Archives for Admin » Page 2
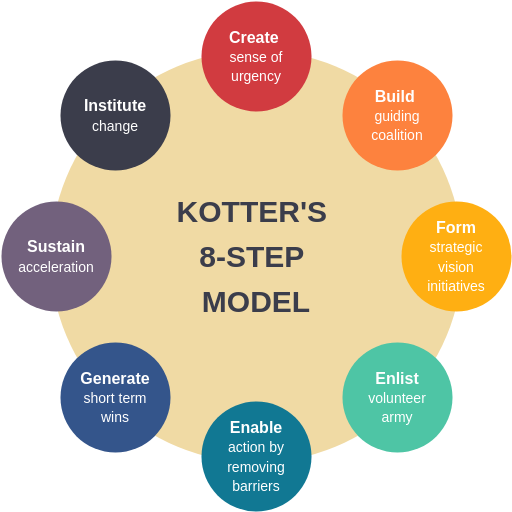
The 8 steps in the process of change include: creating a sense of urgency, forming powerful guiding coalitions, developing a vision and a strategy, communicating the vision, removing obstacles and empowering employees for action, creating short-term wins, consolidating gains and strengthening change by anchoring change in the culture. Kotter’s 8 step model can be explained with the help of the illustration given below:
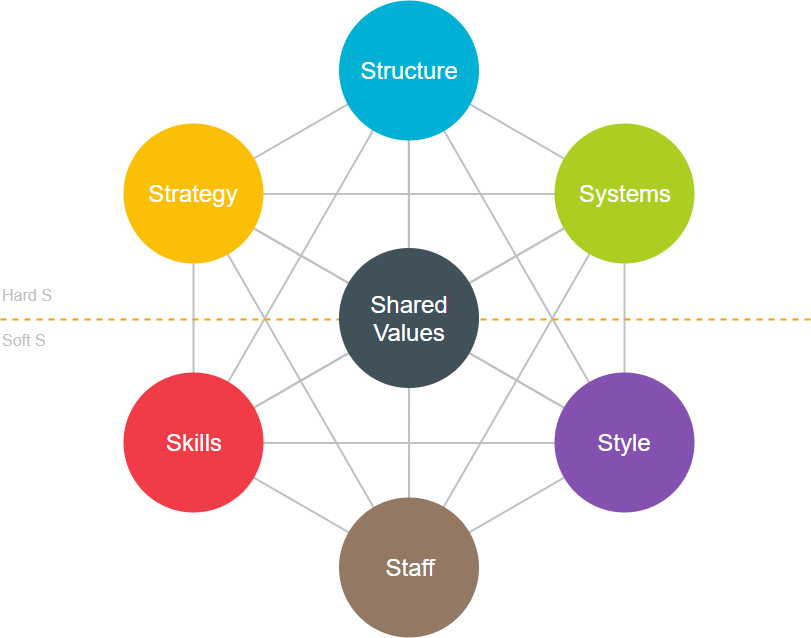
The 7-S model states that all aspects of a company must be considered holistically in the development process. It includes structure, systems, style, staff, skills, strategy and shared values. In other words, it is not enough for a company to have a clear strategy and a well-thought-out action plan, because companies can also make mistakes in the process of implementing their strategies. This is because strategy is only one factor.
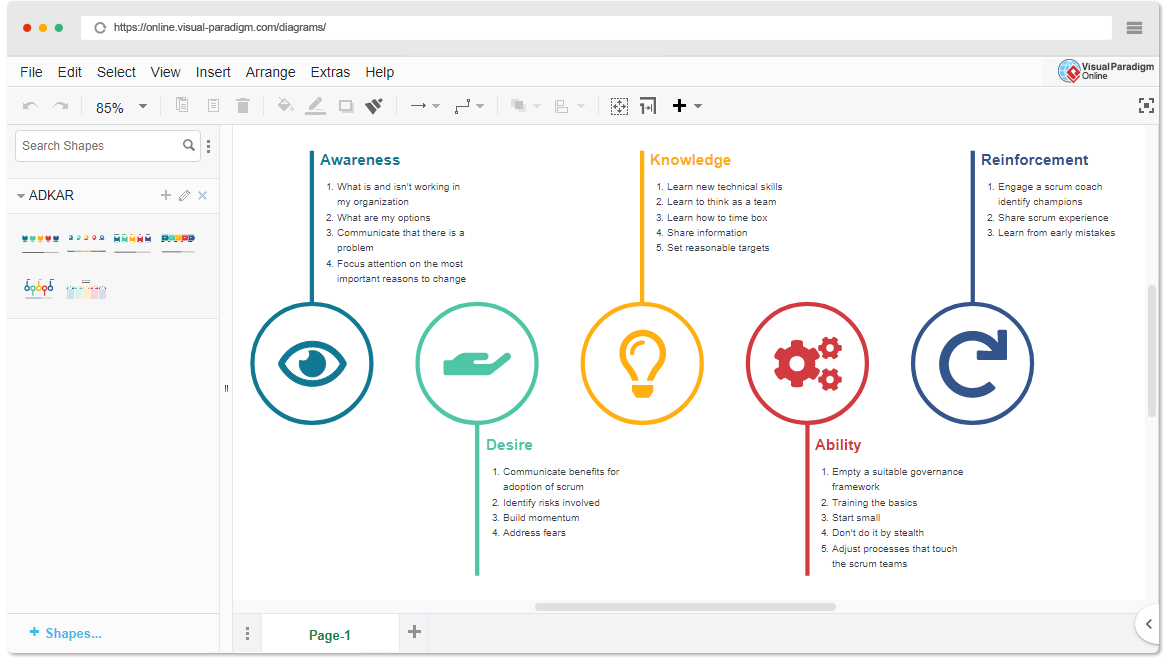
Change is often a complex and difficult process, and more importantly, it is inevitable. Managing change at the individual and organizational levels requires new ideas, new models of change, and new frameworks and tools to successfully achieve the desired change. ADKAR can be applied to all forms of change to drive successful change programs. The ADKAR Transformation Model, created by Prosci founder Jeff Hiatt, consists of five initials that represent the five stages of change an individual must reach to succeed. Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement.
The McKinsey 7S Model ( also known as 7S Model for short) is the seven elements of a business organization designed by the McKinsey & Company Research Center, which states that companies must consider all aspects of the development process in a comprehensive manner, including structure, systems, style, staff, skills, strategy, and shared values - the seven skills, strategies, and shared values.
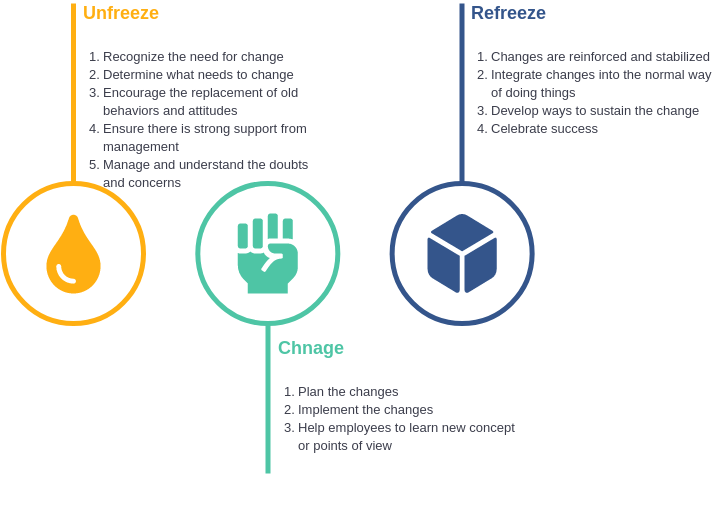
Many models have been developed to explain organizational change. One of the earliest models was developed by Kurt Lewin, a German psychologist and researcher on communication and organizational development. Lewin's three-step approach views change as a break in organizational equilibrium, or a thaw. Once the thaw is complete, the change itself can be introduced, but simply introducing the change does not ensure that the change will last; the new state needs to be refrozen. The new state needs to be refrozen so that it can be maintained for a significant period of time. Thus, the purpose of refreezing is to stabilize the new state by balancing the two forces of driving and binding forces.
-
Posted on February 11, 2022
-
/Under UML
UML Sequence Diagrams are interaction diagrams that detail how operations are carried out. They capture the interaction between objects in the context of a collaboration. Sequence Diagrams are time focus and they show the order of the interaction visually by using the vertical axis of the diagram to represent time what messages are sent and when.
Lewin's Change Management Model is a comprehensive change model designed to understand why change happens and what must be done to effect change in the most seamless way. Lewin developed the change model as a way to illustrate how people react when faced with change in their lives. Lewin's change management model can be applied in a wide range of contexts. For example, it can help you understand why some people and organizations are motivated more by the need for social recognition than by financial incentives, and it teaches you how to engage employees in important organizational change.
-
Posted on February 10, 2022
-
/Under UML
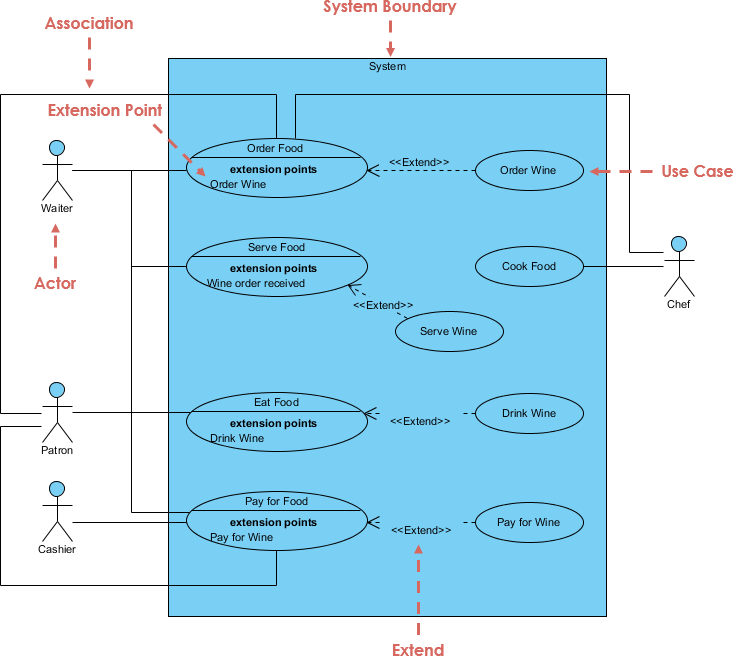
A use case diagram is a Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram for requirements elicitation. Use case diagrams provide a graphical overview of the goals (modeled by use cases) that users (represented by actors) want to achieve by using the system. Use cases in a use case diagram can be organized and arranged according to their relevance, level of abstraction, and impact on the user. They can be linked to show their dependencies, include, extend, generation relationships.
-
Posted on February 10, 2022
-
/Under UML
In UML, relationships are connections between model elements. Use cases are also connected to each other in different kinds of relationships. The relationship between two use cases basically models the dependencies between two use cases. By reusing existing use cases using different types of relationships, the overall effort required to develop the system is reduced. Use case diagrams show use cases, actors, and the relationships between them. For example, the relationship between an actor and a use case illustrates that the actor can use a certain functionality of the business system.
-
Posted on February 9, 2022
-
/Under UML
Use case relationships model the dependencies between use cases in the interaction model of the system. Although, independent use cases can adequately represent simpler systems. However, in order to represent complex or large systems, we may need to construct complex use cases with the help of dependencies between use cases. Establishing relationships between use cases allows reuse of those use cases that need to be defined over and over again, which reduces developer effort.